Use of Capacities
Storyboard 
Capacitance are short-distance metal plates that can be charged by connecting to a potential difference. In this way there is a plate with negative charges (electrons) and the other positive (lack of electrons so that the positive charges of the conductor structure predominate) that are held in place by the attraction between charges of different signs. Once both poles are connected by means of a conductor, current flows until it is completely discharged, the load being equalized on both plates.
ID:(816, 0)
Two plates with opposite charges
Definition 
In the case of two plates with opposite charges there is a field of greater intensity between them. However, there is a minor field that can be described with field lines that emerge from one of the plates and return by giving an external turn to the opposite plate:
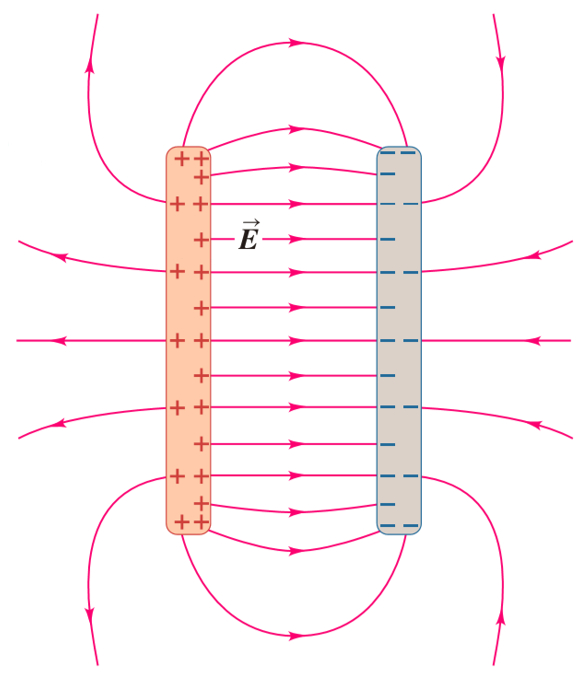
ID:(11454, 0)
Use of Capacities
Description 
Capacitance are short-distance metal plates that can be charged by connecting to a potential difference. In this way there is a plate with negative charges (electrons) and the other positive (lack of electrons so that the positive charges of the conductor structure predominate) that are held in place by the attraction between charges of different signs. Once both poles are connected by means of a conductor, current flows until it is completely discharged, the load being equalized on both plates.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
In the case of two plates with opposite charges there is a field of greater intensity between them. However, there is a minor field that can be described with field lines that emerge from one of the plates and return by giving an external turn to the opposite plate:

(ID 11454)
Si se define una superficie que pasa entre las placas y rodea la carga
$E_dS=\displaystyle\frac{Q}{\epsilon\epsilon_0}$
con
Como por otro lado el campo es igual a la diferencia de potencial
$\Delta\varphi = \displaystyle\frac{\sigma}{\epsilon\epsilon_0}d=E_dd=\displaystyle\frac{Q}{\epsilon\epsilon_0}\displaystyle\frac{d}{S}$
se obtiene con la definici n
$\Delta\varphi=\displaystyle\frac{Q}{C}$
que la capacidad de dos placas se puede calcular con
| $ C = \epsilon_0 \epsilon \displaystyle\frac{ S }{ d }$ |
(ID 3865)
The potential difference ($\Delta\varphi$) generates the charge in the capacitor, inducing the charge ($Q$) on each side (with opposite signs), depending on the capacitor capacity ($C$), according to the following relationship:
| $ \Delta\varphi =\displaystyle\frac{ Q }{ C }$ |
(ID 3864)
ID:(816, 0)
