Intercept at constant speed
Storyboard 
Objects can intersect when they coincide in position at the same moment. To achieve this, they must move from their respective starting points with velocities that enable them to coincide in position and time at the end of the journey.
ID:(445, 0)
Mechanisms
Definition 
During the process of intersection, two bodies move in such a way that they coincide at the intersection position ($s$) and the intersection time ($t$).
For this to occur, each body must start from its initial position and time, with displacements of the first stage speed ($v_1$) and the first stage speed ($v_1$) respectively, such that the coincidence occurs.
ID:(15394, 0)
Concept of intercept
Image 
In the case of interception, two bodies move in such a way that they will coincide at ERROR:10259.1 in their the intersection position ($s$).
For this purpose, each body:
• Starts at the initial time of first object ($t_1$) with the initial position of first object ($s_1$) as its initial position and the first stage speed ($v_1$) as its displacement.
• Starts at the initial time of second object ($t_2$) with the initial position of second object ($s_2$) as its initial position and the second stage speed ($v_2$) as its displacement.
These conditions must be met for the interception to occur.
This allows the diagrams of position over time to be coupled as shown in the following representation:
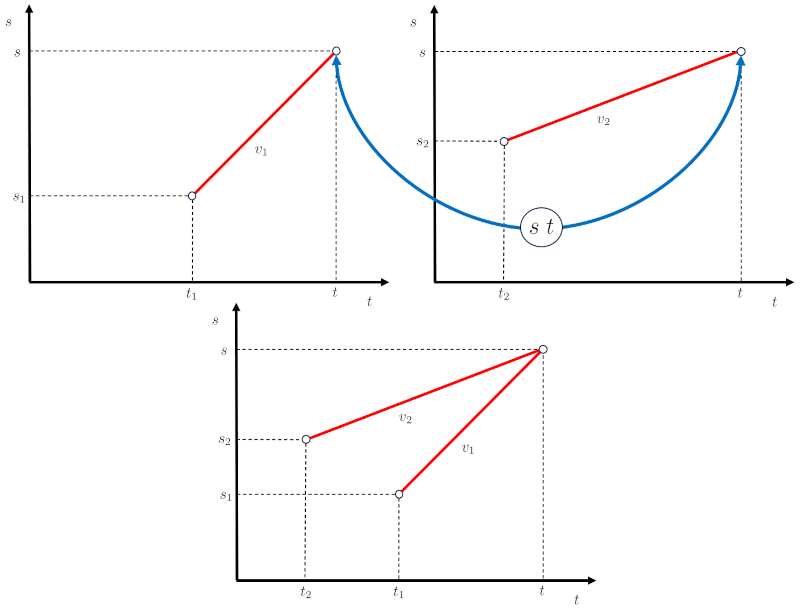
ID:(15505, 0)
Paths and travel durations
Note 
In the case of an intersection or collision between two objects, it's common that the first stage speed ($v_1$) and the second stage speed ($v_2$) must be such that coincidence occurs.
This means that the distance traveled by first object ($\Delta s_1$) and the travel time of first object ($\Delta t_1$) must result in a first stage speed ($v_1$),
| $ v_1 \equiv\displaystyle\frac{ \Delta s_1 }{ \Delta t_1 }$ |
such that with the distance traveled by the second object ($\Delta s_2$) and the travel time of second object ($\Delta t_2$), we obtain a second stage speed ($v_2$),
| $ v_2 \equiv\displaystyle\frac{ \Delta s_2 }{ \Delta t_2 }$ |
so that they ultimately coincide in time and space (position):

ID:(12509, 0)
Position and time when intercepting
Quote 
In the case of a movement where two objects intersect, such as the intersection position ($s$) and the intersection time ($t$), it is common for both. Therefore, if for the first object, the initial time of first object ($t_1$) and the initial position of first object ($s_1$) with the first stage speed ($v_1$) fulfill:
| $ s = s_1 + v_1 ( t - t_1 )$ |
and for the second object, the initial time of second object ($t_2$) and the initial position of second object ($s_2$) with the second stage speed ($v_2$) fulfill:
| $ s = s_2 + v_2 ( t - t_2 )$ |
which is represented as:
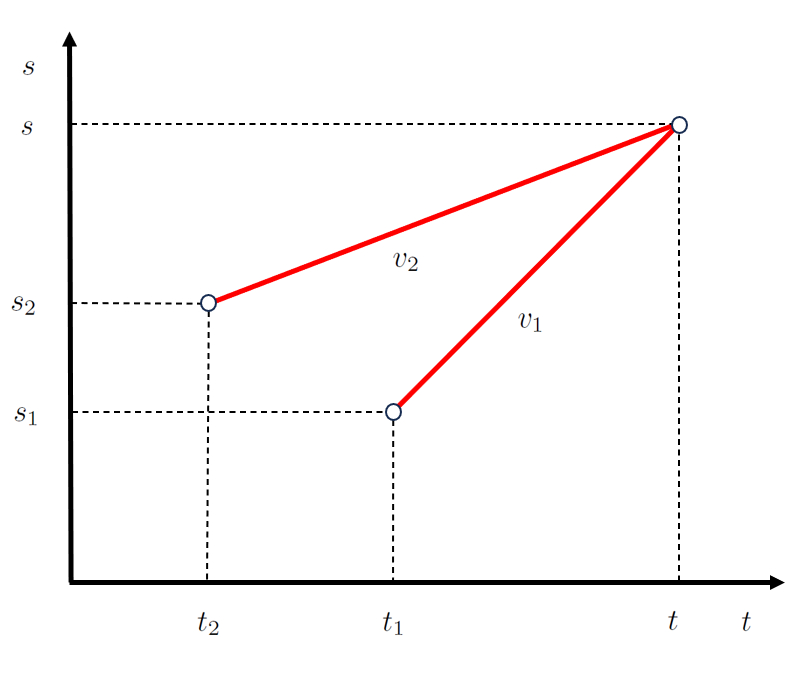
ID:(12510, 0)
Model
Exercise 
The key is that both objects meet at the intersection position ($s$) at time the intersection time ($t$). For this to happen, object 1 starts its journey at the initial position of first object ($s_1$) at ERROR:10252.1 with a velocity of ERROR:10238.1, while object 2 begins its journey at the initial position of second object ($s_2$) at ERROR:10253.1 with a velocity of ERROR:10239.1. During this process, object 1 travels ERROR:10254.1 at ERROR:10256.1, while object 2 travels ERROR:10255.1 at ERROR:10257.1:
ID:(15392, 0)
Intercept at constant speed
Storyboard 
Objects can intersect when they coincide in position at the same moment. To achieve this, they must move from their respective starting points with velocities that enable them to coincide in position and time at the end of the journey.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
With the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$) it is with the position ($s$) and the starting position ($s_0$):
and the time elapsed ($\Delta t$) is with the time ($t$) and the start Time ($t_0$):
The equation for average velocity:
can be written as:
$v_0 = \bar{v} = \displaystyle\frac{\Delta s}{\Delta t} = \displaystyle\frac{s - s_0}{t - t_0}$
thus, solving for it we get:
With the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$) it is with the position ($s$) and the starting position ($s_0$):
and the time elapsed ($\Delta t$) is with the time ($t$) and the start Time ($t_0$):
The equation for average velocity:
can be written as:
$v_0 = \bar{v} = \displaystyle\frac{\Delta s}{\Delta t} = \displaystyle\frac{s - s_0}{t - t_0}$
thus, solving for it we get:
Examples
During the process of intersection, two bodies move in such a way that they coincide at the intersection position ($s$) and the intersection time ($t$).
For this to occur, each body must start from its initial position and time, with displacements of the first stage speed ($v_1$) and the first stage speed ($v_1$) respectively, such that the coincidence occurs.
In the case of interception, two bodies move in such a way that they will coincide at ERROR:10259.1 in their the intersection position ($s$).
For this purpose, each body:
• Starts at the initial time of first object ($t_1$) with the initial position of first object ($s_1$) as its initial position and the first stage speed ($v_1$) as its displacement.
• Starts at the initial time of second object ($t_2$) with the initial position of second object ($s_2$) as its initial position and the second stage speed ($v_2$) as its displacement.
These conditions must be met for the interception to occur.
This allows the diagrams of position over time to be coupled as shown in the following representation:
In the case of an intersection or collision between two objects, it's common that the first stage speed ($v_1$) and the second stage speed ($v_2$) must be such that coincidence occurs.
This means that the distance traveled by first object ($\Delta s_1$) and the travel time of first object ($\Delta t_1$) must result in a first stage speed ($v_1$),
such that with the distance traveled by the second object ($\Delta s_2$) and the travel time of second object ($\Delta t_2$), we obtain a second stage speed ($v_2$),
so that they ultimately coincide in time and space (position):
In the case of a movement where two objects intersect, such as the intersection position ($s$) and the intersection time ($t$), it is common for both. Therefore, if for the first object, the initial time of first object ($t_1$) and the initial position of first object ($s_1$) with the first stage speed ($v_1$) fulfill:
and for the second object, the initial time of second object ($t_2$) and the initial position of second object ($s_2$) with the second stage speed ($v_2$) fulfill:
which is represented as:
The key is that both objects meet at the intersection position ($s$) at time the intersection time ($t$). For this to happen, object 1 starts its journey at the initial position of first object ($s_1$) at ERROR:10252.1 with a velocity of ERROR:10238.1, while object 2 begins its journey at the initial position of second object ($s_2$) at ERROR:10253.1 with a velocity of ERROR:10239.1. During this process, object 1 travels ERROR:10254.1 at ERROR:10256.1, while object 2 travels ERROR:10255.1 at ERROR:10257.1:
We can calculate the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$) from the starting position ($s_0$) and the position ($s$) using the following equation:
We can calculate the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$) from the starting position ($s_0$) and the position ($s$) using the following equation:
To describe the motion of an object, we need to calculate the time elapsed ($\Delta t$). This magnitude is obtained by measuring the start Time ($t_0$) and the the time ($t$) of said motion. The duration is determined by subtracting the initial time from the final time:
To describe the motion of an object, we need to calculate the time elapsed ($\Delta t$). This magnitude is obtained by measuring the start Time ($t_0$) and the the time ($t$) of said motion. The duration is determined by subtracting the initial time from the final time:
The mean Speed ($\bar{v}$) can be calculated from the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$) and the time elapsed ($\Delta t$) using:
The mean Speed ($\bar{v}$) can be calculated from the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$) and the time elapsed ($\Delta t$) using:
If the speed is constant, the velocity will be equal to the initial Speed ($v_0$). In this case, the distance traveled as a function of time can be calculated using the difference between the position ($s$) and the starting position ($s_0$), divided by the difference between the time ($t$) and the start Time ($t_0$):
The corresponding equation defines a straight line in space-time.
If the speed is constant, the velocity will be equal to the initial Speed ($v_0$). In this case, the distance traveled as a function of time can be calculated using the difference between the position ($s$) and the starting position ($s_0$), divided by the difference between the time ($t$) and the start Time ($t_0$):
The corresponding equation defines a straight line in space-time.
ID:(445, 0)
