Flow of an incompressible liquid
Storyboard 
When a liquid is in motion, we refer to it as flow, and its measurement is based on the volume that passes through a section in a given period of time. Assuming that the volume moves without deformation, the velocity at which the liquid passes through the section remains constant. In this case, flow can also be defined as the product of velocity and the cross-sectional area.
ID:(875, 0)
Flow of an incompressible liquid
Storyboard 
When a liquid is in motion, we refer to it as flow, and its measurement is based on the volume that passes through a section in a given period of time. Assuming that the volume moves without deformation, the velocity at which the liquid passes through the section remains constant. In this case, flow can also be defined as the product of velocity and the cross-sectional area.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Flow is defined as the volume the volume element ($\Delta V$) divided by time the time elapsed ($\Delta t$), which is expressed in the following equation:
and the volume equals the cross-sectional area the section Tube ($S$) multiplied by the distance traveled the tube element ($\Delta s$):
Since the distance traveled the tube element ($\Delta s$) per unit time the time elapsed ($\Delta t$) corresponds to the velocity, it is represented by:
Thus, the flow is a flux density ($j_s$), which is calculated using:
Flow is defined as the volume the volume element ($\Delta V$) divided by time the time elapsed ($\Delta t$), which is expressed in the following equation:
and the volume equals the cross-sectional area the section Tube ($S$) multiplied by the distance traveled the tube element ($\Delta s$):
Since the distance traveled the tube element ($\Delta s$) per unit time the time elapsed ($\Delta t$) corresponds to the velocity, it is represented by:
Thus, the flow is a flux density ($j_s$), which is calculated using:
Examples
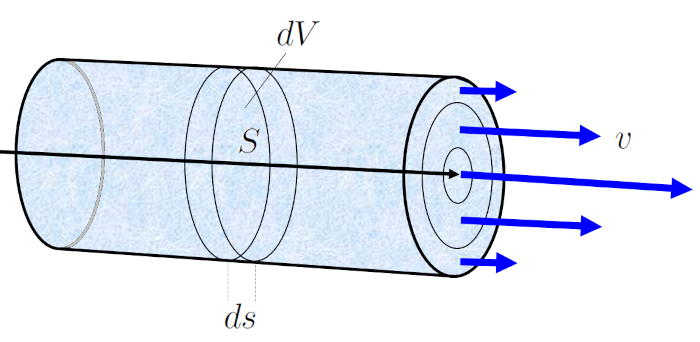
During a time elapsed ($\Delta t$), the fluid with a mean Speed of Fluid ($v$) moves a tube element ($\Delta s$). If the section ($S$) represents the amount of fluid crossing that section in the time elapsed ($\Delta t$), it is calculated as:
$\Delta V = S \Delta s = Sv \Delta t$
This equation states that the volume of fluid flowing through section the section ($S$) during a time elapsed ($\Delta t$) is equal to the product of the cross-sectional area and the distance the fluid travels during that time.
This facilitates the calculation of the volume element ($\Delta V$), which is the volume of fluid flowing through the channel in a specific period of the time elapsed ($\Delta t$), corresponding to the volume flow ($J_V$).
Flow is defined as the volume the volume element ($\Delta V$) divided by time the time elapsed ($\Delta t$), which is expressed in the following equation:
and the volume equals the cross-sectional area the section Tube ($S$) multiplied by the distance traveled the tube element ($\Delta s$):
Since the distance traveled the tube element ($\Delta s$) per unit time the time elapsed ($\Delta t$) corresponds to the velocity, it is represented by:
Thus, the flow is a flux density ($j_s$), which is calculated using:
It is important to note that in this model:
The flow density acts as an average velocity across the entire flow section.
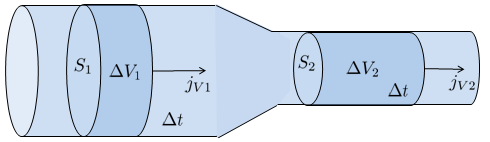
Considering a tube that neither leaks nor receives additional liquid, the flow entering at point 1 The volume flow 1 ($J_{V1}$) will be equal to the flow exiting at point 2 The volume flow 2 ($J_{V2}$):
Within a channel or tube, there may be a change in cross-sectional area, either widening or narrowing.
This variation will directly affect the flow through the flux density ($j_s$), which represents the velocity, increasing (if the section narrows) or decreasing (if it widens) according to the section Tube ($S$) to keep the volume flow ($J_V$) constant, as indicated by:
The conservation of flow, along with the definition of flow density, leads to the conservation law such that the section in point 1 ($S_1$), the section in point 2 ($S_2$), the flux density 1 ($j_{s1}$), and the flux density 2 ($j_{s2}$) satisfy:
The continuity equation assumes that the flow is uniform, with no reverse flows or turbulence present. Therefore, it is necessary to verify that the flow is indeed laminar and free of turbulence, especially when applying the equation to analyze fluid flows in pipes and channels.
There are various methods for detecting turbulence in the flow, such as using flow meters or visually observing the flow. It is essential to ensure that the flow is stable before applying the continuity equation, as any disturbance in the flow can affect the accuracy of the calculations and the overall efficiency of the system.
If we have a tube with a the section Tube ($S$) moving a distance the tube element ($\Delta s$) along its axis, having displaced the volume element ($\Delta V$), then it is equal to:
If we have a tube with a the section Tube ($S$) moving a distance the tube element ($\Delta s$) along its axis, having displaced the volume element ($\Delta V$), then it is equal to:
The volume flow ($J_V$) corresponds to the volume flowing ($\Delta V$) flowing through the channel at the time elapsed ($\Delta t$). Therefore, we have:
The volume flow ($J_V$) corresponds to the volume flowing ($\Delta V$) flowing through the channel at the time elapsed ($\Delta t$). Therefore, we have:
The flux density ($j_s$) is related to the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$), which is the distance that the fluid travels in the time elapsed ($\Delta t$), as follows:
The flux density ($j_s$) is related to the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$), which is the distance that the fluid travels in the time elapsed ($\Delta t$), as follows:
A flux density ($j_s$) can be expressed in terms of the volume flow ($J_V$) using the section or Area ($S$) through the following formula:
A flux density ($j_s$) can be expressed in terms of the volume flow ($J_V$) using the section or Area ($S$) through the following formula:
One of the most basic laws in physics is the conservation of mass, which holds true throughout our macroscopic world. Only in the microscopic world does a conversion between mass and energy exist, which we will not consider in this case. In the case of a fluid, this means that the mass entering through a pipe must be equal to the mass exiting it.
If density is constant, the same applies to volume. In such cases, when we treat the flow as an incompressible fluid, it means that a given volume entering one end of the pipe must exit the other end. This can be expressed as the equality between the flow in Position 1 ($J_1$) and the flow in Position 2 ($J_2$), with the equation:
The surface of a disk ($S$) of ERROR:5275.1 is calculated as follows:
The surface of a disk ($S$) of ERROR:5275.1 is calculated as follows:
The principle of continuity dictates that the flow at the first point, which is equal to the flux density 1 ($j_{s1}$) times the section in point 1 ($S_1$), must be equal to the flow at the second point, given by the flux density 2 ($j_{s2}$) times the section in point 2 ($S_2$). From this, it follows that:
ID:(875, 0)