Internal energy and partition function
Image 
The internal energy is allowed to calculate from the partition function as the derivative with respect to
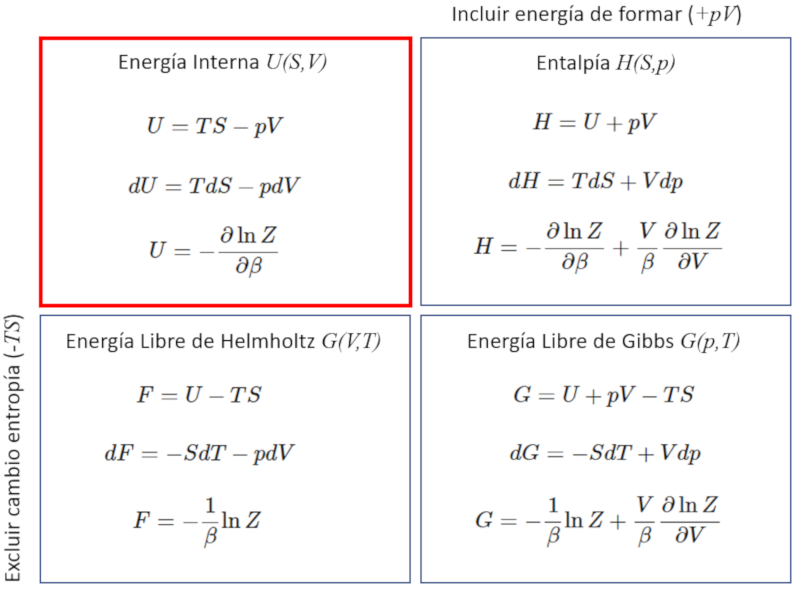
ID:(11723, 0)
