Enthalpy and partition function
Image 
The enthalpy can be calculated from the partition function if it is remembered that this is equal to the internal energy and the pressure times the volume:
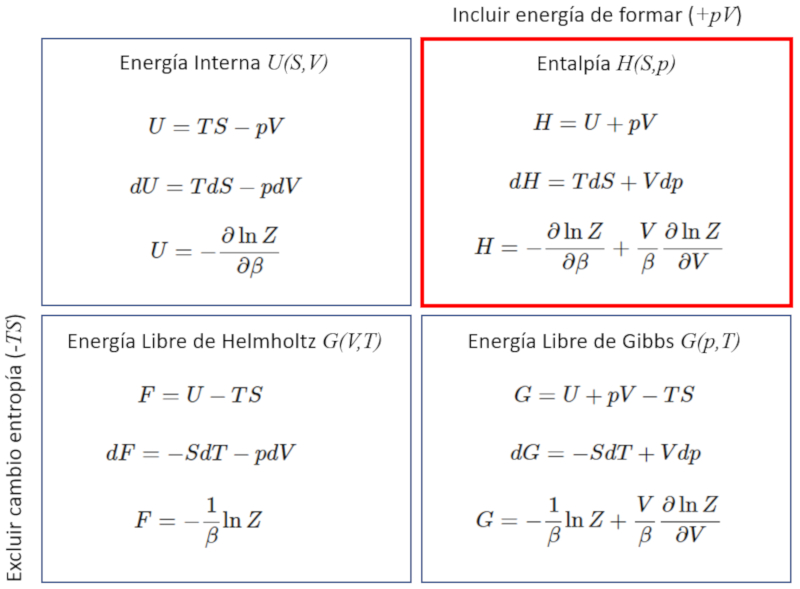
ID:(11724, 0)
