Harmonic oscillator
Storyboard 
With the harmonic oscillator, we can explore the probability of finding a particle within a particular position or velocity range. This helps us understand how phase space is utilized in terms of both momentum and position.
ID:(1558, 0)
Harmonic Oscillator Model
Definition 
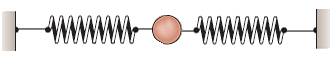
A harmonic oscillator is a system that is exposed to a force proportional to the distance to the equilibrium point that it always opposes when moving away from it. An example of a harmonic oscillator is represented by a mass attached to two springs:
ID:(11462, 0)
Harmonic Oscillator Phase Space Curve
Image 
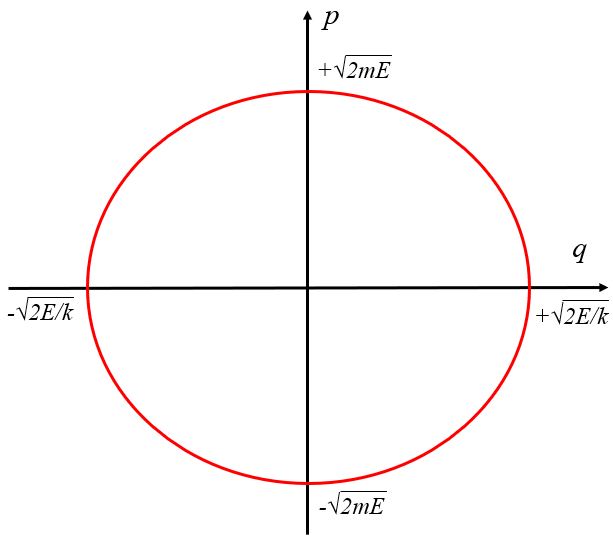
La energía de un oscilador armónico con es
| $ \displaystyle\frac{ p ^2}{ 2 m E }+\displaystyle\frac{ q ^2}{ 2 E / k }=1 $ |
lo que se representa como la elipse que muestra la gráfica:
ID:(11467, 0)
Curved range of the phase space of the harmonic oscillator
Note 
Probability only makes sense insofar as it refers to a range since otherwise it would be null. In the case of the harmonic oscillator, the range in which we seek to study is that of energy, that is, the energy of the system is between

ID:(11468, 0)
Probability of finding the harmonic oscillator in one position
Quote 
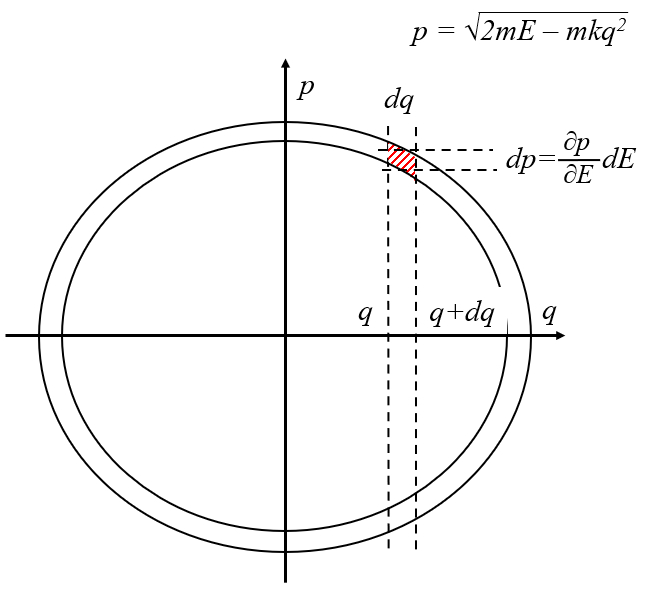
The probability of finding the particle in a position between
ID:(11469, 0)
Probability of finding the harmonic oscillator with a moment
Exercise 
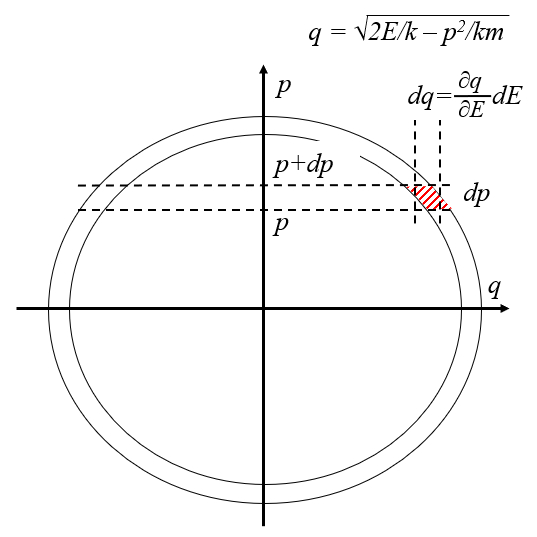
The probability of finding the particle with a memento between
ID:(11470, 0)
Harmonic oscillator
Storyboard 
With the harmonic oscillator, we can explore the probability of finding a particle within a particular position or velocity range. This helps us understand how phase space is utilized in terms of both momentum and position.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
A harmonic oscillator is a system that is exposed to a force proportional to the distance to the equilibrium point that it always opposes when moving away from it. An example of a harmonic oscillator is represented by a mass attached to two springs:
En el caso cl sico de una part cula de masa
La ecuaci n de la energ a del oscilador arm nico con
se puede reescribir en la forma t pica de una ecuaci n de una elipse con
with major axes
and the minor axis
El eje mayor de la elipse del oscilador arm nico en el espacio de fase es con
es con
El eje menor de la elipse del oscilador arm nico en el espacio de fase es con
es igual con
La energ a de un oscilador arm nico con
lo que se representa como la elipse que muestra la gr fica:
Probability only makes sense insofar as it refers to a range since otherwise it would be null. In the case of the harmonic oscillator, the range in which we seek to study is that of energy, that is, the energy of the system is between
Area of an ellipse
The area of an ellipse with
whose major axis is
and whose minor axis is
is calculated using
Using the area of the phase space ellipse for the harmonic oscillator with
the phase space area is obtained by subtracting the area at energy $E+dE$ from the area at energy $E$:
$2 \pi (E + dE)\sqrt{\displaystyle\frac{m}{k}} - 2 \pi E \sqrt{\displaystyle\frac{m}{k}} = 2 \pi E \sqrt{\displaystyle\frac{m}{k}}$
Thus, with
The probability of finding the particle in a position between
Con el rea de la capa con
y la ecuaci n de la elipse con
$dp =\displaystyle\frac{\partial}{\partial E}\sqrt{2 m E - k m q^2} dE =\displaystyle\frac{m}{\sqrt{2 m E - m k q ^2}} dE $
con lo que la probabilidad es con
The probability of finding the particle with a memento between
Con el rea de la capa con
y la ecuaci n de la elipse con
$dq =\displaystyle\frac{\partial}{\partial E}\sqrt{2 E / k - p ^2/ m k } dE=\displaystyle\frac{ m }{\sqrt{2 m E - m k q ^2}} dE$
con lo que la probabilidad es con
ID:(1558, 0)
