Particle in a box and sphere
Storyboard 
When we consider a particle within a volume, whether it's a box or a sphere, we can estimate the probability of finding the particle within a range of positions.
ID:(433, 0)
Phase space of a particle in a box 1D
Definition 
Consider a box of length
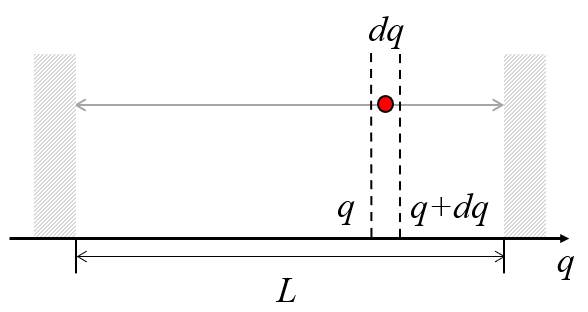
The question is what is the probability of finding it in a
ID:(11463, 0)
Phase space of a particle in a box 2D
Image 
Consider a 2D box of length
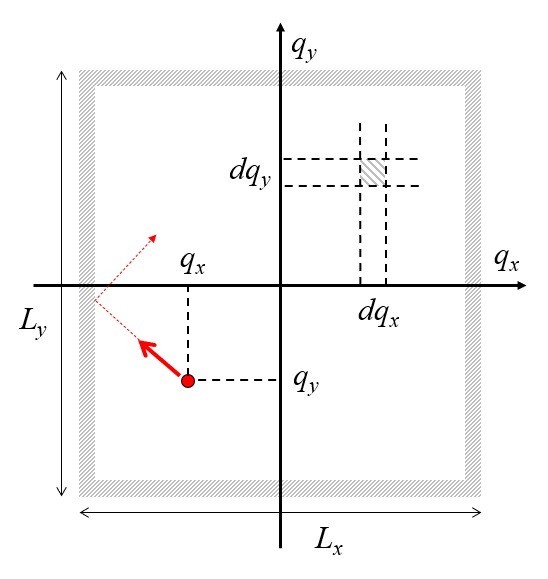
The question is what is the probability of finding it in a quadrilateral of width
ID:(11464, 0)
Phase space of a particle in a 3D sphere
Note 
Consider a sphere of radius
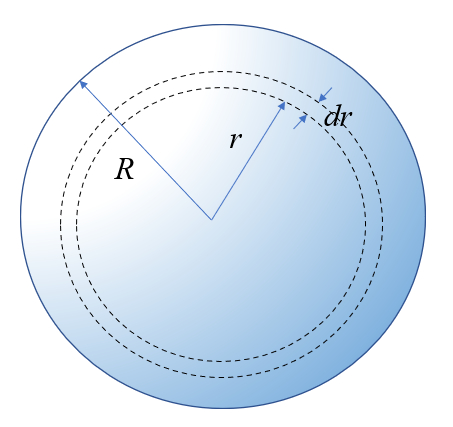
The question is what is the probability of finding it in a quadrilateral of width
ID:(11465, 0)
Probability of finding the particle in a radius $r$
Quote 
La probabilidad de encontrar la partícula en un radio entre
| $ P(r) = \displaystyle\frac{3 r ^2}{ R ^3 } dr $ |
que se muestra en la siguiente gráfica:

ID:(11466, 0)
Particle in a box and sphere
Storyboard 
When we consider a particle within a volume, whether it's a box or a sphere, we can estimate the probability of finding the particle within a range of positions.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
Consider a box of length
The question is what is the probability of finding it in a
Si se asume que la part cula puede estar en cualquiera posici n en una dimensiones, las posiciones posibles son aquellas descritas por el largo
Las posiciones favorables de encontrar la part cula entre
Esto es solo valido si:
Toda posici n es igualmente probable.
lo que se puede generalizar en
Todo estado es igualmente probable.
Adicionalmente se debe notar que la probabilidad esta ntimamente ligada con el rango. Si el rango es nulo, tambi n lo es la probabilidad.
Consider a 2D box of length
The question is what is the probability of finding it in a quadrilateral of width
Si se asume que la part cula puede estar en cualquiera posici n en dos dimensiones, las posiciones posibles son aquellas descritas por los largos de las aristas del rect ngulo.
Por ello la probabilidad de encontrar la part cula en el elemento rectangular son con
Consider a sphere of radius
The question is what is the probability of finding it in a quadrilateral of width
Si se asume que la part cula puede estar en cualquiera posici n tridimensional dentro de una esfera de radio
$4\pi r^2 dr$
\\n\\ndividido por el volumen de la esfera\\n\\n
$\displaystyle\frac{4\pi}{3} R^3$
por lo que con
La probabilidad de encontrar la part cula en un radio entre
que se muestra en la siguiente gr fica:
ID:(433, 0)
