Distribuidor de líquidos
Image 
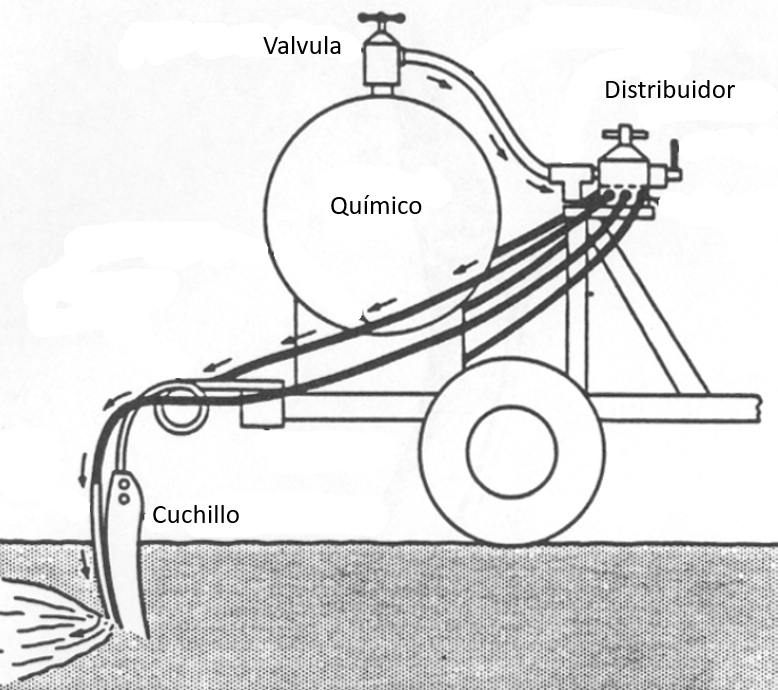
En caso de que se busca introducir el químico como liquido en el suelo se trabaja con un sistema que lleva un estanque y trabaja con un cuchillo de abre la tierra para depositar el liquido:
ID:(12893, 0)
Chemical application
Storyboard 
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
The volume flow ($J_V$) can be calculated from the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) and the pressure difference ($\Delta p$) using the following equation:
Furthermore, using the relationship for the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$):
results in:
Since the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$) is equal to the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) as per the following equation:
and since the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) is expressed in terms of the viscosity ($\eta$), the tube radius ($R$), and the tube length ($\Delta L$) as follows:
we can conclude that:
Examples
The resistance is defined in terms of the fluid viscosity and the sphere's velocity as follows:
Stokes explicitly calculated the resistance experienced by the sphere and determined that viscosity is proportional to the sphere's radius and its velocity, leading to the following equation for resistance:
Al pulverizar los l quidos se obtiene los droplets:
En caso de que se busca introducir el qu mico como liquido en el suelo se trabaja con un sistema que lleva un estanque y trabaja con un cuchillo de abre la tierra para depositar el liquido:
Darcy rewrites the Hagen Poiseuille equation so that the pressure difference ($\Delta p$) is equal to the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$) times the volume flow ($J_V$):
Since the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$) is equal to the inverse of the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$), it can be calculated from the expression of the latter. In this way, we can identify parameters related to geometry (the tube length ($\Delta L$) and the tube radius ($R$)) and the type of liquid (the viscosity ($\eta$)), which can be collectively referred to as a hydraulic resistance ($R_h$):
ID:(1685, 0)