Poisson distributions
Storyboard 
In the case where the probability is very small, the binomial distribution is reduced to a Poisson distribution.
ID:(1555, 0)
Example comparison with Poisson distribution
Definition 
If we study the binomial distribution for large numbers
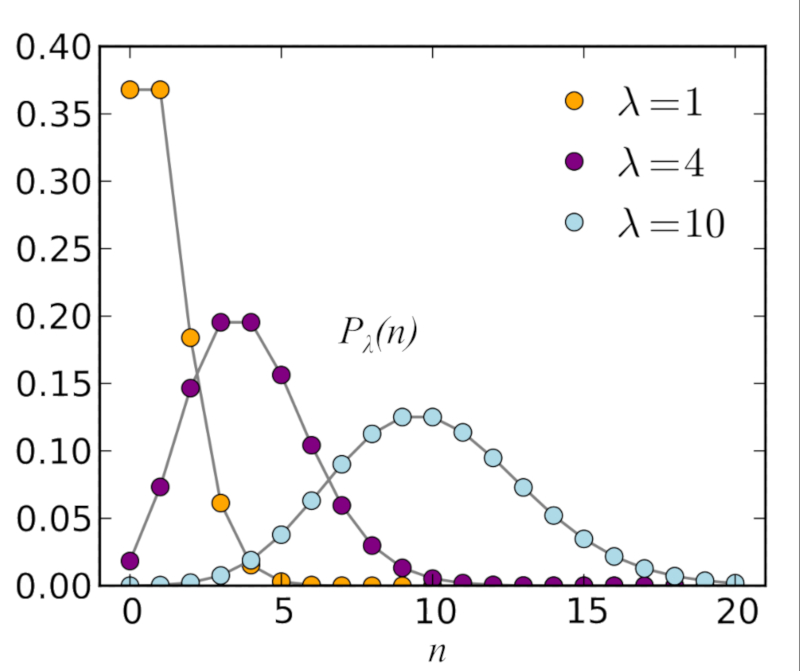
ID:(7794, 0)
Poisson distributions
Storyboard 
In the case where the probability is very small, the binomial distribution is reduced to a Poisson distribution.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
Con
con
y solo existe la probabilidad de ir a la derecha o a la izquierda, con
por lo que con
Therefore expressions such as
with what you get with
that is
With the approximation
and employing
it can be shown that
How the exponential is defined as
and by entering
you can replace
Since the probability of taking
for a large number
and
the binomial distribution is reduced to a Poisson distribution:
If we study the binomial distribution for large numbers
ID:(1555, 0)
