Radiation type
Storyboard 
For modeling it is convenient to separate the radiation into a wavelength component up to 750 nm (VIS or visible) and one over said wavelength (NIR or near infrared or simply infrared). This is because albedo tends to have very different values for low wavelengths and above that value.
ID:(860, 0)
Spectrum of the sun on earth
Image 
La luz del sol al llegar a la tierra tiene el tipico espectro de cuerpo negro. Sin embargo al penetrar la atmosfera pierde parte de su intensidad en función de las absorcioens que sufre.
Si se observa el espectro de luz solar se nota que abarca tres rangos:
* ultra violeta (200 a 380 nm)
* visible (380 a 750 nm)
* infraroja (750 a 2500 nm)

Balance de Radiación Visible
ID:(8083, 0)
Principales flujos de radiación
Image 
La radiación que incide sobre el planeta es radiación visible y es reflejada y absorbida por atmósfera y superficie del planeta. El reflejo lo vemos como radiación visible y da origen a las fotos del planeta que se han sacado desde el espacio exterior. La fracción absorbida lleva a un calentamiento del planeta y de la atmósfera que genera emisiones de radiación infrarroja (calor). A estos flujo se suman mecanismos de convección y transporte.
Los distintos flujos y estimaciones de la energía por área y tiempo estimados se resumen en el siguiente diagrama:
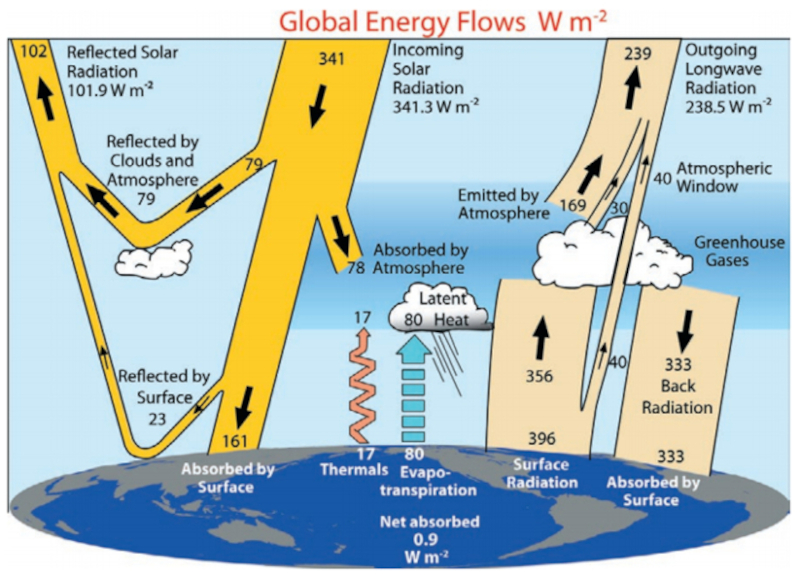
En primera aproximación se puede asumir que la superficie del planeta es homogénea, es decir los albedos y coberturas son constantes sobre la superficie. Dentro de este esquema se tiene un modelo unidimensional (D1) en que solo se estudia en mayor detalle el comportamiento de la atmósfera y se pueden estimar los parámetros del modelo.
ID:(9286, 0)
Radiation range
Image 
Radiation is divided into that from the sun (mostly visible) and that from the earth (mostly infrared). When represented as a function of wavelength, it appears as follows:

Typical satellite measurements, such as those from the MODIS project, are taken in different channels.
The visible part is measured with three channels:
| Channels | Ranges [µm] | Relative Weights |
| Blue | 0.459-0.479 | 0.4364 |
| Green | 0.545-0.565 | 0.2366 |
| Red | 0.620-0.670 | 0.3265 |
The infrared part is estimated with the following channels:
| Channels | Ranges [µm] | Relative Weights |
| NIR | 0.841-0.876 | 0.5447 |
| 1.2 | 1.230-1.250 | 0.1363 |
| 1.6 | 1.628-1.652 | 0.0469 |
| 2.1 | 2.105-2.155 | 0.2536 |
The results from the first group are referred to as VIS, while those from the second group are referred to as NIR, although part of the observed spectrum falls within the visible range.
To understand why the separation is made around 750 nm instead of 3 microns, as is normally defined for the infrared range, one must consider the behavior of the albedo. It shows a substantial increase for wavelengths around 750 nm and above, not just from 3 microns onwards (see the albedo chart as a function of wavelength).
ID:(9921, 0)
Dependence of albedo on wavelength
Image 
Si uno observa el comportamiento del albedo en función del largo deonda nota que este, para las superficies típcas varia en forma dramática entre el rango visible y el infrarrojo.

Balance de Radiación Visible
Por ello da sentido separar el espectro en torno a un largo de onda en torno a 750nm o sea hablar de radiación mayormente visible o del tipo infrarrojo. Hay que hacer notar que bajo "luz visible" estamos tambien incluyendo una parte del espectro ultravioleta ya que tambien hay radiación significante en largos de onda inferiores a los 380 nm.
ID:(8084, 0)
Infrared radiation (NIR)
Condition 
In climate models, radiation is divided into two ranges that have different origins and behaviors.
In the case of radiation with wavelengths greater than
which partially covers the infrared spectrum, it is called Near Infrared (NIR) radiation and originates from both the Earth's surface and the atmosphere.
ID:(9950, 0)
Visible radiation (VIS)
Condition 
In climate models, radiation is divided into two ranges that have different origins and behaviors.
In the case of radiation with wavelengths shorter than
which includes a portion of the visible and ultraviolet spectrum, it is referred to as visible radiation (VIS) and originates from the Sun.
ID:(9951, 0)
Emisión onda larga de la tierra en función del tiempo (D0+1)
Php 
Si se observa la radiación de onda larga (NIR) se ve que existe un máximo en torno al mes de agosto/septiembre de todos los años:
Esto se debe a que el hemisferio norte presenta mayor masas continentales por lo que estas reflejan mayormente cuando es verano en dicho hemisferio..
ID:(9324, 0)
Emisión onda larga de la tierra en función de la latitud (D1+0)
Php 
La radiación de onda larga (NIR) es en primera aproximación simétrica en torno al ecuador fuera de presentar un máximo en torno de los grados -20 y +20:
Esto corresponde tanto a la falta de masa continental en torno al ecuador y la baja de intensidad hacia los polos por efecto de la incidencia inclinada de la radiación.
ID:(9325, 0)
