Multivariate Time Series (LSTM)
Storyboard 
The climatic parameter model to forecast the evolution of pollution levels
Code and data
ID:(1794, 0)
Load libreries
Description 
Load libreries:
from math import sqrt from numpy import concatenate from matplotlib import pyplot from pandas import read_csv from pandas import DataFrame from pandas import concat from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense from keras.layers import LSTM
ID:(13898, 0)
Load data
Description 
Load data:
# load dataset
dataset = read_csv('pollution.csv', header=0, index_col=0)
values = dataset.values
print(dataset)pollution dew temp press wnd_dir wnd_spd snow rain
date
2010-01-02 00:00:00 129.0 -16 -4.0 1020.0 SE 1.79 0 0
2010-01-02 01:00:00 148.0 -15 -4.0 1020.0 SE 2.68 0 0
2010-01-02 02:00:00 159.0 -11 -5.0 1021.0 SE 3.57 0 0
2010-01-02 03:00:00 181.0 -7 -5.0 1022.0 SE 5.36 1 0
2010-01-02 04:00:00 138.0 -7 -5.0 1022.0 SE 6.25 2 0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
2014-12-31 19:00:00 8.0 -23 -2.0 1034.0 NW 231.97 0 0
2014-12-31 20:00:00 10.0 -22 -3.0 1034.0 NW 237.78 0 0
2014-12-31 21:00:00 10.0 -22 -3.0 1034.0 NW 242.70 0 0
2014-12-31 22:00:00 8.0 -22 -4.0 1034.0 NW 246.72 0 0
2014-12-31 23:00:00 12.0 -21 -3.0 1034.0 NW 249.85 0 0
[43800 rows x 8 columns]
ID:(13899, 0)
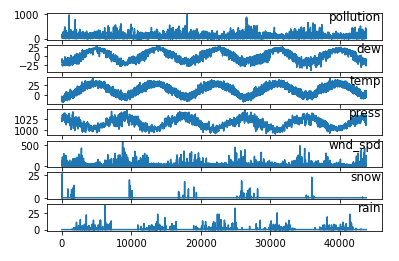
Show data
Description 
Load data:
from matplotlib import pyplot
# specify columns to plot
groups = [0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7]
i = 1
# plot each column
pyplot.figure()
for group in groups:
pyplot.subplot(len(groups), 1, i)
pyplot.plot(values[:, group])
pyplot.title(dataset.columns[group], y=0.5, loc='right')
i += 1
pyplot.show()
ID:(13900, 0)
Prepare the series
Description 
Prepare the series to train the model:
# convert series to supervised learning
def series_to_supervised(data, n_in=1, n_out=1, dropnan=True):
n_vars = 1 if type(data) is list else data.shape[1]
df = DataFrame(data)
cols, names = list(), list()
# input sequence (t-n, ... t-1)
for i in range(n_in, 0, -1):
cols.append(df.shift(i))
names += [('var%d(t-%d)' % (j+1, i)) for j in range(n_vars)]
# forecast sequence (t, t+1, ... t+n)
for i in range(0, n_out):
cols.append(df.shift(-i))
if i == 0:
names += [('var%d(t)' % (j+1)) for j in range(n_vars)]
else:
names += [('var%d(t+%d)' % (j+1, i)) for j in range(n_vars)]
# put it all together
agg = concat(cols, axis=1)
agg.columns = names
# drop rows with NaN values
if dropnan:
agg.dropna(inplace=True)
return agg
ID:(13901, 0)
Enencode data
Description 
The data of the wnd_dir wind is in the classes according to the direction or the absence of this.
# integer encode direction encoder = LabelEncoder() values[:,4] = encoder.fit_transform(values[:,4])
ID:(13902, 0)
Convert and scale data
Description 
The data is converted into real numbers using the astype ('float32') function and then scaled with the MinMaxScaler function between 0 and 1.
# ensure all data is float
values = values.astype('float32')
# normalize features
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
scaled = scaler.fit_transform(values)
ID:(13903, 0)
Temporarily offset the series
Description 
Form series with time lag:
# specify the number of lag hours n_hours = 3 n_features = 8 # frame as supervised learning reframed = series_to_supervised(scaled, n_hours, 1) print(reframed)
var1(t-3) var2(t-3) var3(t-3) var4(t-3) var5(t-3) var6(t-3) \
3 0.129779 0.352941 0.245902 0.527273 0.666667 0.002290
4 0.148893 0.367647 0.245902 0.527273 0.666667 0.003811
5 0.159960 0.426471 0.229508 0.545454 0.666667 0.005332
6 0.182093 0.485294 0.229508 0.563637 0.666667 0.008391
7 0.138833 0.485294 0.229508 0.563637 0.666667 0.009912
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
43795 0.008048 0.250000 0.311475 0.745455 0.333333 0.365103
43796 0.009054 0.264706 0.295082 0.763638 0.333333 0.377322
43797 0.010060 0.264706 0.278689 0.763638 0.333333 0.385730
43798 0.008048 0.250000 0.278689 0.781818 0.333333 0.395659
43799 0.010060 0.264706 0.262295 0.781818 0.333333 0.405588
var7(t-3) var8(t-3) var1(t-2) var2(t-2) ... var7(t-1) var8(t-1) \
3 0.000000 0.0 0.148893 0.367647 ... 0.000000 0.0
4 0.000000 0.0 0.159960 0.426471 ... 0.037037 0.0
5 0.000000 0.0 0.182093 0.485294 ... 0.074074 0.0
6 0.037037 0.0 0.138833 0.485294 ... 0.111111 0.0
7 0.074074 0.0 0.109658 0.485294 ... 0.148148 0.0
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
43795 0.000000 0.0 0.009054 0.264706 ... 0.000000 0.0
43796 0.000000 0.0 0.010060 0.264706 ... 0.000000 0.0
43797 0.000000 0.0 0.008048 0.250000 ... 0.000000 0.0
43798 0.000000 0.0 0.010060 0.264706 ... 0.000000 0.0
43799 0.000000 0.0 0.010060 0.264706 ... 0.000000 0.0
var1(t) var2(t) var3(t) var4(t) var5(t) var6(t) var7(t) \
3 0.182093 0.485294 0.229508 0.563637 0.666667 0.008391 0.037037
4 0.138833 0.485294 0.229508 0.563637 0.666667 0.009912 0.074074
5 0.109658 0.485294 0.213115 0.563637 0.666667 0.011433 0.111111
6 0.105634 0.485294 0.213115 0.581818 0.666667 0.014492 0.148148
7 0.124748 0.485294 0.229508 0.600000 0.666667 0.017551 0.000000
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
43795 0.008048 0.250000 0.278689 0.781818 0.333333 0.395659 0.000000
43796 0.010060 0.264706 0.262295 0.781818 0.333333 0.405588 0.000000
43797 0.010060 0.264706 0.262295 0.781818 0.333333 0.413996 0.000000
43798 0.008048 0.264706 0.245902 0.781818 0.333333 0.420866 0.000000
43799 0.012072 0.279412 0.262295 0.781818 0.333333 0.426216 0.000000
var8(t)
3 0.0
4 0.0
5 0.0
6 0.0
7 0.0
... ...
43795 0.0
43796 0.0
43797 0.0
43798 0.0
43799 0.0
[43797 rows x 32 columns]
ID:(13904, 0)
Separate data into train and test set
Description 
Separate data into a set to train train and to evaluate test :
# split into train and test sets values = reframed.values n_train_hours = 365 * 24 train = values[:n_train_hours, :] test = values[n_train_hours:, :]
ID:(13905, 0)
Separate data on input and output
Description 
Separate data into a set to train train and to evaluate test :
# split into input and outputs n_obs = n_hours * n_features train_X, train_y = train[:, :n_obs], train[:, -n_features] test_X, test_y = test[:, :n_obs], test[:, -n_features] print(train_X.shape, len(train_X), train_y.shape)
(8760, 24) 8760 (8760,)
ID:(13906, 0)
Restructure data according to data, times and factors
Description 
Restructure data according to data, times and factors:
# reshape input to be 3D [samples, timesteps, features] train_X = train_X.reshape((train_X.shape[0], n_hours, n_features)) test_X = test_X.reshape((test_X.shape[0], n_hours, n_features)) print(train_X.shape, train_y.shape, test_X.shape, test_y.shape)
(8760, 3, 8) (8760,) (35037, 3, 8) (35037,)
ID:(13907, 0)
Define and configure the model
Description 
Define and configure the model:
# design network pollution_model = Sequential() pollution_model.add(LSTM(50, input_shape=(train_X.shape[1], train_X.shape[2]))) pollution_model.add(Dense(1)) pollution_model.compile(loss='mae', optimizer='adam')
ID:(13908, 0)
Train the model
Description 
Train the model:
# fit network history = pollution_model.fit(train_X, train_y, epochs=50, batch_size=72, validation_data=(test_X, test_y), verbose=2, shuffle=False)
Epoch 1/50
122/122 - 3s - loss: 0.0584 - val_loss: 0.0514
Epoch 2/50
122/122 - 1s - loss: 0.0297 - val_loss: 0.0364
Epoch 3/50
122/122 - 1s - loss: 0.0217 - val_loss: 0.0232
...
Epoch 48/50
122/122 - 1s - loss: 0.0141 - val_loss: 0.0144
Epoch 49/50
122/122 - 1s - loss: 0.0145 - val_loss: 0.0140
Epoch 50/50
122/122 - 1s - loss: 0.0143 - val_loss: 0.0136
ID:(13909, 0)
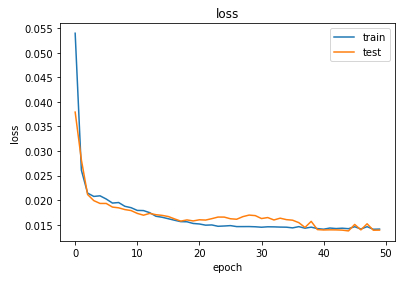
Show loss function
Description 
Show loss function:
# plot history
pyplot.plot(history.history['loss'], label='train')
pyplot.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label='test')
plt.title('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('loss')
pyplot.legend()
pyplot.show()
ID:(13910, 0)
Calculate predicted values
Description 
Calculate predicted values:
# make a prediction
yhat = pollution_model.predict(test_X)
test_X = test_X.reshape((test_X.shape[0], n_hours*n_features))
# invert scaling for forecast
inv_yhat = concatenate((yhat, test_X[:, -7:]), axis=1)
inv_yhat = scaler.inverse_transform(inv_yhat)
inv_yhat = inv_yhat[:,0]
# invert scaling for actual
test_y = test_y.reshape((len(test_y), 1))
inv_y = concatenate((test_y, test_X[:, -7:]), axis=1)
inv_y = scaler.inverse_transform(inv_y)
inv_y = inv_y[:,0]
# calculate RMSE
rmse = sqrt(mean_squared_error(inv_y, inv_yhat))
print('Test RMSE: %.3f' % rmse)Test RMSE: 26.357
ID:(13911, 0)
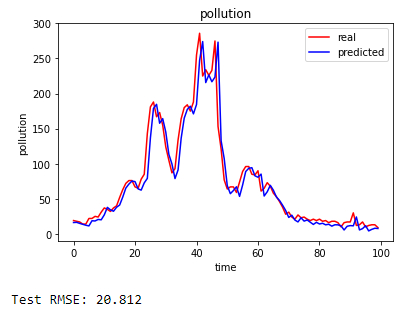
Show predicted values
Description 
Show predicted values:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Visualising the results
sub_y = inv_y[0:100]
sub_yhat = inv_yhat[0:100]
plt.plot(sub_y, color = 'red', label = 'real')
plt.plot(sub_yhat, color = 'blue', label = 'predicted')
plt.title('pollution')
plt.xlabel('time')
plt.ylabel('pollution')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# calculate RMSE
rmse = sqrt(mean_squared_error(sub_y, sub_yhat))
print('Test RMSE: %.3f' % rmse)
ID:(13912, 0)
