Refraction when crossing a Flat Body
Storyboard 
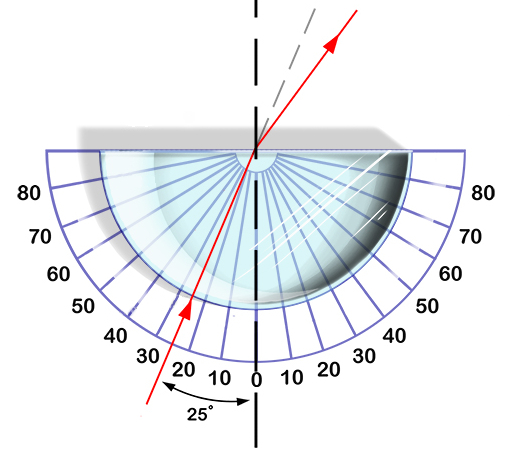
When the beam strikes a flat medium of defined interposed thickness, it penetrates with a different angle of refraction from the incident. This may be both greater and less than the angle of incidence depending on the respective refractive indices. Once the beam reaches the second edge of the medium, the process is reversed so that the beam returns to its original direction, only out of date.
ID:(1375, 0)
Refraction when crossing a Flat Body
Description 
When the beam strikes a flat medium of defined interposed thickness, it penetrates with a different angle of refraction from the incident. This may be both greater and less than the angle of incidence depending on the respective refractive indices. Once the beam reaches the second edge of the medium, the process is reversed so that the beam returns to its original direction, only out of date.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Como la relaci n entre los ngulos de incidencia y refracci n es
| $\displaystyle\frac{ \sin \theta_i }{\sin \theta_r }=\displaystyle\frac{ c_i }{ c_e }$ |
y el indice de refracci n se define como
| $ n =\displaystyle\frac{ c }{ v }$ |
\\n\\nse tiene que con\\n\\n
$n_i=\displaystyle\frac{c}{c_i}$
y\\n\\n
$n_e=\displaystyle\frac{c}{c_e}$
\\n\\nque\\n\\n
$\displaystyle\frac{c_i}{c_e}=\displaystyle\frac{c_i}{c}\displaystyle\frac{c}{c_e}=\displaystyle\frac{n_e}{n_i}=\displaystyle\frac{\sin\theta_i}{\sin\theta_e}$
por lo que resulta
| $ n_i \sin \theta_i = n_e \sin \theta_r $ |
(ID 3343)
Examples
La ley de Snell para el paso de la luz de un medio de indice
| $ n_i \sin \theta_i = n_e \sin \theta_r $ |
(ID 3343)
Paso de la luz por un objeto
(ID 1853)
Para calcular la distancia
Para obtener
y se puede obtener
Con ello se obtiene
| $ d = h \displaystyle\frac{\sin( \theta_1 - \theta_2 )}{\cos \theta_1 }$ |
(ID 3345)
ID:(1375, 0)
