Colors and Photons
Storyboard 
Light, in its corpuscular picture, is described by introducing a particle that we call the photon.
Its color is a reflection of its energy being the frequency of this directly proportional to this.
ID:(668, 0)
The spectre
Image 
As the angle of refraction depends on the frequency or wavelength of light in glass, a prism can be used to decompose light into its different colors.
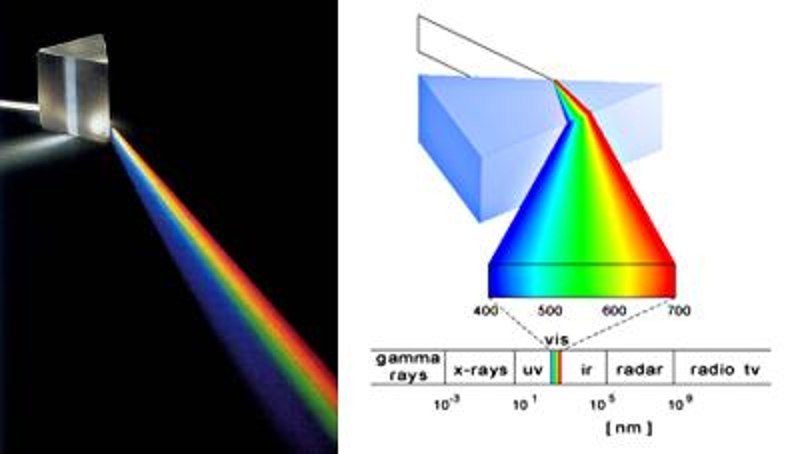
This results in what we call the spectrum of light.
ID:(6972, 0)
Photon energy
Equation 
The color of light is associated with its the photon frequency ($\nu$), and there is a direct relationship between this frequency and the photon energy ($\epsilon$):
$E$
Photon energy
$J$
5141
$\nu$
Photon frequency
$Hz$
5564
$h$
Planck constant
6.62607004e-34
$J s$
5142
where the planck constant ($h$) has a value of $6.62\times 10^{-34} , \text{Js}$.
ID:(3341, 0)
