Dissolution of salt in the ocean
Definition 
The ions in the salt dissociate and are surrounded by water molecules forming clusters of a size greater than that of the original ion:
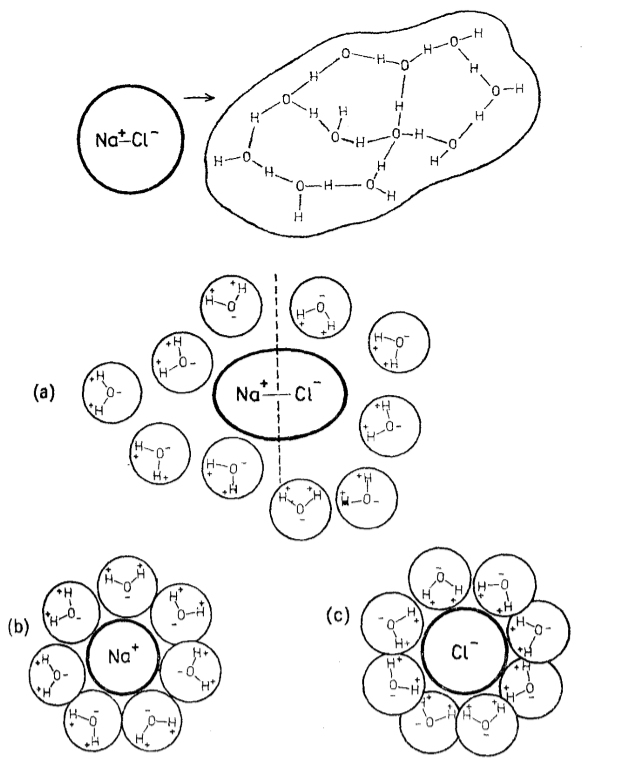
ID:(11991, 0)
Salt ion hydrate
Image 
Once the ion is surrounded by water molecules, a second layer of molecules is formed, which are linked by bridges:
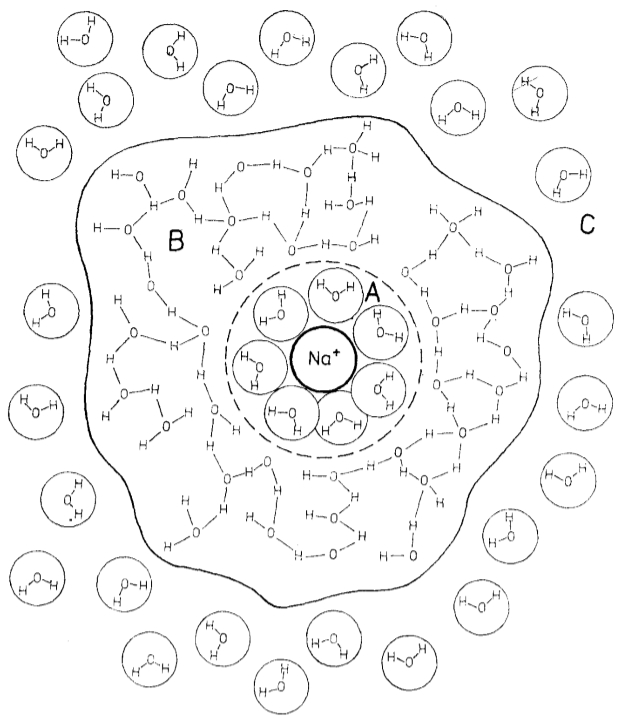
ID:(11992, 0)
Electric field acts on ion hydrate of salt
Note 
If an electric field is applied to water with salt ions, the latter begin to move towards the positive poles:
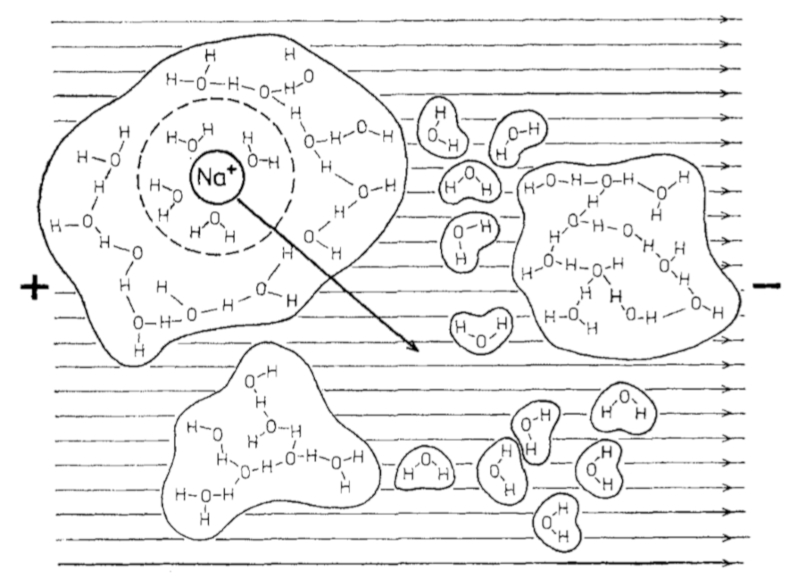
ID:(11993, 0)
Electrical conductivity as a function of salinity
Quote 
The electrical conductivity as a function of salinity and temperature that is explained by the greater presence of ions and the greater mobility at higher temperatures:
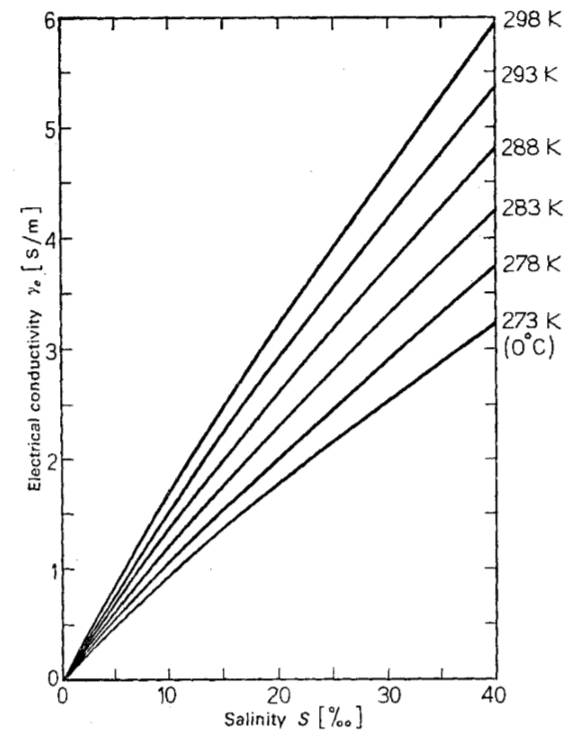
ID:(11994, 0)
Electrical conductivity as a function of pressure
Exercise 
Electrical conductivity as a function of pressure and temperature:

ID:(11995, 0)
Values of electrical conductivity as a function of salinity
Equation 
The following table shows electrical conductivity as a function of salinity:

ID:(11996, 0)
Electrical Conductivity in Ocean Water
Storyboard 
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
The ions in the salt dissociate and are surrounded by water molecules forming clusters of a size greater than that of the original ion:
Once the ion is surrounded by water molecules, a second layer of molecules is formed, which are linked by bridges:
If an electric field is applied to water with salt ions, the latter begin to move towards the positive poles:
The electrical conductivity as a function of salinity and temperature that is explained by the greater presence of ions and the greater mobility at higher temperatures:
Electrical conductivity as a function of pressure and temperature:
The specific conductivity measured in seawater under atmospheric pressure can be empirically represented as
The following table shows electrical conductivity as a function of salinity:
Dado que la resistencia del agua marina depende de su salinidad, se puede medir la resistencia para determinar el nivel de salinidad. Esto se hace comparando las conductividades de una muestra de agua marina con una soluci n standard de KCl (clorato de potasio). Se miden la conductividad especifica de ambas muestras a una temperatura de 15C y 1 atm de presi n y establece la relaci n\\n\\n
$K=\sqrt{\displaystyle\frac{\gamma_w}{\gamma_{KCl}}}$
y calcula la salinidad con
con
a_0=0.0080
a_1=-0.1692
a_2=25.3851
a_3=14.0941
a_4=-7.0261
a_5=2.7081
ID:(1619, 0)
