Modell für Aktien (RNN)
Storyboard 
Das Aktienmodell nimmt historische Segmente und den Wert, der ihnen folgt, und versucht, das Muster zu erkennen und nach jeder Sequenz abzuleiten, wie es weitergeht.
Code und Daten
ID:(1792, 0)
Bibliotheken importieren
Beschreibung 
Importieren der erforderlichen Bibliotheken:
# importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
ID:(13872, 0)
Lade Daten
Beschreibung 
Laden Sie historische Aktienkurse von Google:
# load stock prices
dataset_train = pd.read_csv('stock_price_train.csv')
print(dataset_train)Date Open High Low Close Volume
0 1/3/2012 325.25 332.83 324.97 663.59 7,380,500
1 1/4/2012 331.27 333.87 329.08 666.45 5,749,400
2 1/5/2012 329.83 330.75 326.89 657.21 6,590,300
3 1/6/2012 328.34 328.77 323.68 648.24 5,405,900
4 1/9/2012 322.04 322.29 309.46 620.76 11,688,800
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
1253 12/23/2016 790.90 792.74 787.28 789.91 623,400
1254 12/27/2016 790.68 797.86 787.66 791.55 789,100
1255 12/28/2016 793.70 794.23 783.20 785.05 1,153,800
1256 12/29/2016 783.33 785.93 778.92 782.79 744,300
1257 12/30/2016 782.75 782.78 770.41 771.82 1,770,000
[1258 rows x 6 columns]
ID:(13873, 0)
Eröffnungspreise extrahieren
Beschreibung 
Bilden einer Vereinbarung mit den Daten der Eröffnungskurse der Aktie:
# extract opening prices train = dataset_train.loc[:, ['Open']].values train
array([[325.25],
[331.27],
[329.83],
...,
[793.7 ],
[783.33],
[782.75]])
ID:(13874, 0)
Werte neu skalieren
Beschreibung 
Um die Lernqualität zu verbessern, werden die Werte zwischen 0 und 1 neu skaliert:
# feature scaling from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range = (0, 1)) train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(train) train_scaled
array([[0.08581368],
[0.09701243],
[0.09433366],
...,
[0.95725128],
[0.93796041],
[0.93688146]])
ID:(13875, 0)
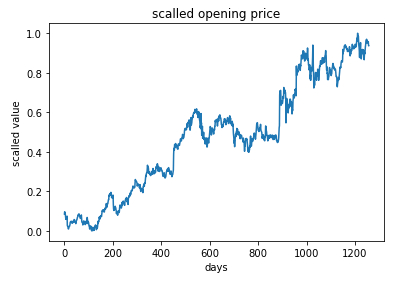
Werte anzeigen
Beschreibung 
Die Werte können zeitlich dargestellt werden:
# show data
plt.plot(train_scaled)
plt.title('scalled opening price')
plt.xlabel('days')
plt.ylabel('scalled value')
plt.show()
ID:(13876, 0)
Segmente erstellen
Beschreibung 
Zur Modellierung werden 1208 Folgen von 50 X_train Werten und dem folgenden y_train Wert extrahiert:
# creating a data structure with 50 timesteps and 1 output
X_train = []
y_train = []
timesteps = 50
for i in range(timesteps, 1258):
X_train.append(train_scaled[i-timesteps:i, 0])
y_train.append(train_scaled[i, 0])
X_train, y_train = np.array(X_train), np.array(y_train)
ID:(13877, 0)
Werte nachordnen
Beschreibung 
Ordnen der Trainingswerte mit der Funktion np.reshape trainieren neu an:
# reshaping
X_train = np.reshape(X_train, (X_train.shape[0], X_train.shape[1], 1))
print(X_train.shape[0],',',X_train.shape[1],',',y_train.shape[0])
print('X_train=',X_train)
print('y_train=',y_train)1208 , 50 , 1208
X_train= [[[0.08581368]
[0.09701243]
[0.09433366]
...
[0.03675869]
[0.04486941]
[0.05065481]]
...
[[0.96569685]
[0.97510976]
[0.95966962]
...
[0.95163331]
[0.95725128]
[0.93796041]]]
y_train= [0.05214302 ... 0.93688146]
ID:(13878, 0)
Modell definieren, trainieren und trainieren
Beschreibung 
Das Modell ist als Sequential() sequentielles Modell definiert, vier SimpleRNN Layer werden mit der Funktion add und ein abschließender Einzelelementlayer hinzugefügt. Das Modell wird mit dem Befehl compile strukturiert und anschließend mit dem Befehl fit trainiert:
# importing the Keras libraries and packages from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense from keras.layers import SimpleRNN from keras.layers import Dropout # initialising the RNN regressor = Sequential() # adding the first RNN layer and some Dropout regularisation regressor.add(SimpleRNN(units = 50,activation='tanh', return_sequences = True, input_shape = (X_train.shape[1], 1))) regressor.add(Dropout(0.2)) # adding a second RNN layer and some Dropout regularisation regressor.add(SimpleRNN(units = 50,activation='tanh', return_sequences = True)) regressor.add(Dropout(0.2)) # adding a third RNN layer and some Dropout regularisation regressor.add(SimpleRNN(units = 50,activation='tanh', return_sequences = True)) regressor.add(Dropout(0.2)) # adding a fourth RNN layer and some Dropout regularisation regressor.add(SimpleRNN(units = 50)) regressor.add(Dropout(0.2)) # adding the output layer regressor.add(Dense(units = 1)) # compiling the RNN regressor.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'mean_squared_error') # fitting the RNN to the Training set regressor.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs = 100, batch_size = 32)
Epoch 1/100
38/38 [==============================] - 17s 20ms/step - loss: 0.4512
Epoch 2/100
38/38 [==============================] - 1s 19ms/step - loss: 0.2486
Epoch 3/100
38/38 [==============================] - 1s 18ms/step - loss: 0.1825
...
Epoch 98/100
38/38 [==============================] - 1s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0021
Epoch 99/100
38/38 [==============================] - 1s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0022
Epoch 100/100
38/38 [==============================] - 1s 18ms/step - loss: 0.0022
ID:(13879, 0)
Daten zur Auswertung laden
Beschreibung 
Laden Sie die Google-Aktienkurse für 2017, um sie mit den prognostizierten Preisen zu vergleichen:
# load real stock prices (2017)
dataset_test = pd.read_csv('stock_price_test.csv')
print(dataset_test)Date Open High Low Close Volume
0 1/3/2017 778.81 789.63 775.80 786.14 1,657,300
1 1/4/2017 788.36 791.34 783.16 786.90 1,073,000
2 1/5/2017 786.08 794.48 785.02 794.02 1,335,200
3 1/6/2017 795.26 807.90 792.20 806.15 1,640,200
4 1/9/2017 806.40 809.97 802.83 806.65 1,272,400
5 1/10/2017 807.86 809.13 803.51 804.79 1,176,800
6 1/11/2017 805.00 808.15 801.37 807.91 1,065,900
7 1/12/2017 807.14 807.39 799.17 806.36 1,353,100
8 1/13/2017 807.48 811.22 806.69 807.88 1,099,200
9 1/17/2017 807.08 807.14 800.37 804.61 1,362,100
10 1/18/2017 805.81 806.21 800.99 806.07 1,294,400
11 1/19/2017 805.12 809.48 801.80 802.17 919,300
12 1/20/2017 806.91 806.91 801.69 805.02 1,670,000
13 1/23/2017 807.25 820.87 803.74 819.31 1,963,600
14 1/24/2017 822.30 825.90 817.82 823.87 1,474,000
15 1/25/2017 829.62 835.77 825.06 835.67 1,494,500
16 1/26/2017 837.81 838.00 827.01 832.15 2,973,900
17 1/27/2017 834.71 841.95 820.44 823.31 2,965,800
18 1/30/2017 814.66 815.84 799.80 802.32 3,246,600
19 1/31/2017 796.86 801.25 790.52 796.79 2,160,600
ID:(13880, 0)
Extrahieren der Eröffnungspreise zur Bewertung
Beschreibung 
Formularanordnung mit den Daten der Eröffnungskurse der Aktion zur Auswertung:
# extract opening prices para evaluar real_stock_price = dataset_test.loc[:, ['Open']].values real_stock_price
array([[778.81],
[788.36],
[786.08],
[795.26],
[806.4 ],
[807.86],
[805. ],
[807.14],
[807.48],
[807.08],
[805.81],
[805.12],
[806.91],
[807.25],
[822.3 ],
[829.62],
[837.81],
[834.71],
[814.66],
[796.86]])
ID:(13881, 0)
Werte zur Auswertung neu skalieren
Beschreibung 
Zum Vergleich werden die Bewertungswerte im Bereich 0 und 1 skaliert:
# getting the predicted stock price of 2017 dataset_total = pd.concat((dataset_train['Open'], dataset_test['Open']), axis = 0) inputs = dataset_total[len(dataset_total) - len(dataset_test) - timesteps:].values.reshape(-1,1) inputs = scaler.transform(inputs) # min max scaler inputs
array([[0.97510976],
[0.95966962],
[0.97808617],
...
[1.03354044],
[0.99624228],
[0.9631297 ]])
ID:(13882, 0)
Prognosepreise
Beschreibung 
Die Eingabewerte werden zu den X_text Testwerten geformt und mit der Predict Funktion werden die Werte vorhergesagt:
X_test = []
for i in range(timesteps, 70):
X_test.append(inputs[i-timesteps:i, 0])
X_test = np.array(X_test)
X_test = np.reshape(X_test, (X_test.shape[0], X_test.shape[1], 1))
predicted_stock_price = stock_regressor.predict(X_test)
predicted_stock_price = scaler.inverse_transform(predicted_stock_price)
print(predicted_stock_price)[[791.3195 ]
[788.87964]
[789.0553 ]
[791.17883]
[793.6802 ]
[796.1757 ]
[798.198 ]
[799.31714]
[799.56616]
[799.31494]
[799.6199 ]
[799.514 ]
[798.5145 ]
[798.20874]
[798.54846]
[800.562 ]
[803.8723 ]
[807.5642 ]
[809.4684 ]
[807.31573]]
ID:(13883, 0)
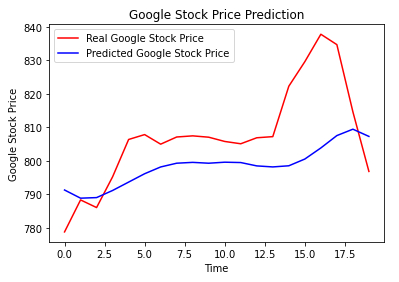
Vergleichen Sie vorhergesagte Werte mit tatsächlichen Werten
Beschreibung 
Abschließend werden die prognostizierten und tatsächlichen Werte angezeigt:
# Visualising the results
plt.plot(real_stock_price, color = 'red', label = 'Real Google Stock Price')
plt.plot(predicted_stock_price, color = 'blue', label = 'Predicted Google Stock Price')
plt.title('Google Stock Price Prediction')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Google Stock Price')
plt.legend()
plt.show()\
ID:(13884, 0)
