Gaussian distribution
Storyboard 
In the limit of similar probabilities the binomial distribution is reduced in the continuous limit to the Gaussean distribution.
ID:(1556, 0)
Example comparison with Gaussian distribution
Image 
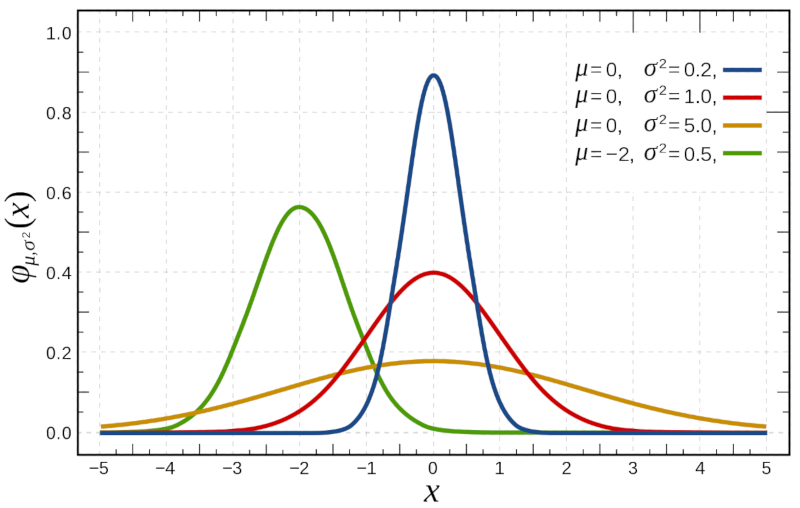
If we study the binomial distribution for large numbers
| $P(x)=\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}e^{-(x-\mu)^2/2\sigma^2}$ |
which is represented below:
ID:(7793, 0)
Gaussian distribution
Model 
In the limit of similar probabilities the binomial distribution is reduced in the continuous limit to the Gaussean distribution.
Variables
Symbol
Text
Variable
Value
Units
Calculate
MKS Value
MKS Units
$\sigma$
sigma
Desviación estándar de Gauss
-
$n$
n
Number
-
$q$
q
Número de pasos hacia la derecha
-
$n_1$
n_1
Número de pasos hacia la izquierda
-
$N$
N
Número total de pasos
-
$n$
n
Número totales de pasos a la izquierda
-
$u$
u
Parameter $u$
-
$s$
s
Posición camino aleatorio
m
$\mu$
mu
Posición media
m
$P_N(m)$
P_Nm
Probabilidad de $n_1$ de $N$ pasos hacia la izquierda
-
$p$
p
Probabilidad de pasos hacia la izquierda
-
$a$
a
Step size
m
Calculations
First, select the equation:  to
to  ,
then, select the variable:
,
then, select the variable:  to
to 
Symbol
Equation
Solved
Translated
Calculations
Symbol
Equation
Solved
Translated
Equations
(ID 8973)
(ID 9008)
Examples
If we study the binomial distribution for large numbers
| $P(x)=\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}e^{-(x-\mu)^2/2\sigma^2}$ |
which is represented below:

(ID 7793)
ID:(1556, 0)
