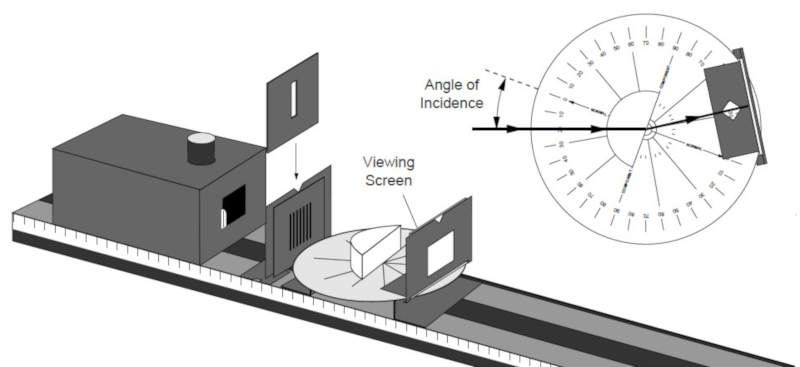
Experiment with Reflection
Storyboard 
Reflection can be studied both with a beam that initially propagates in air (first medium) and is reflected in a mirror (second medium) and in a beam that propagates in glass (first medium) and is reflected in an edge covered by a layer of metal that turns it into a mirror (second medium).
In both cases it is observed that the angle of incidence is identical to that of reflection.
ID:(301, 0)
Projection and Object in Water
Description 
Not being able to perceive the refraction of the beam, objects under water are perceived in a different place than they actually are.
ID:(432, 0)
Total Refraction in Water as seen by an Diver
Image 
If the beam in a medium of less speed tries to move to a medium of greater speed in an angle such that there is no refractive angle this is fully reflected in the interface between both means.
ID:(1852, 0)
Two Mirrors in an Angle
Description 
If two angles are at an angle less than 90 degrees a beam that is reflected in one of these will reach the second.

ID:(9781, 0)
Reflection of Light Objects
Concept 
If you think of light as particles (photon) that affects a non-transparent body, it is reflected.
The reflection occurs so that the angle of insidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
On the other hand, the photons do not change in frequency or wavelength, that is, they only suffer a change in the direction of propagation with respect to the plane of impact.
ID:(195, 0)
Direction of the reflected Light
Equation 
Para la luz reflejada el angulo del haz respecto de la normal
ID:(3262, 0)
Reflection point of the Light in the Mirror
Equation 
For the reflected light the angle of the beam with respect to the normal
ID:(9778, 0)
Angulo de incidencia
Equation 
El angulo de incidencia
ID:(9779, 0)

