Gravitation
Storyboard 
To describe how speed evolves over time, the variation in time must be studied.
The speed variation ratio is equivalent to the curvature of the path traveled in the elapsed time which, divided by this, corresponds to the acceleration.
For a finite elapsed time the speed corresponds to the average acceleration during that time.
ID:(1383, 0)
Gravity with Axis pointing down
Definition 
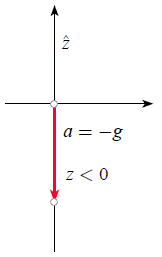
When using a coordinate system with positive z-axis pointing upwards, gravity corresponds to a process of acceleration in the downward direction:

Gravity with axis pointing down
ID:(2249, 0)
Gravity with Axis pointing up
Image 
When using a coordinate system with negative z-axis pointing downwards, gravity corresponds to a process of acceleration in the same direction as the z-axis:
Gravity with axis pointing up
ID:(2250, 0)
Gravitation
Storyboard 
To describe how speed evolves over time, the variation in time must be studied. The speed variation ratio is equivalent to the curvature of the path traveled in the elapsed time which, divided by this, corresponds to the acceleration. For a finite elapsed time the speed corresponds to the average acceleration during that time.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
If an object is described in a coordinate system where the z-axis points upwards (towards the sky), the acceleration experienced by the object is equal to the gravitational acceleration defined as negative, given by
$a = -g < 0$
.
Since the acceleration is constant, the velocity of the object will change linearly, as described by the equation
which simplifies to
in this particular case.
When using a coordinate system with positive z-axis pointing upwards, gravity corresponds to a process of acceleration in the downward direction:
If an object is described in a coordinate system where the z-axis points \"down\" (towards the ground), the acceleration it experiences is equal to the gravitational acceleration, which is defined as positive:
$a = g > 0$
Since the acceleration is constant, the velocity will evolve linearly, as shown in the following equation:
Therefore, in this case, it can be reduced to the following equation:
When using a coordinate system with negative z-axis pointing downwards, gravity corresponds to a process of acceleration in the same direction as the z-axis:
ID:(1383, 0)
