The Diesel Cycle
Storyboard 
The Diesel cycle corresponds to an internal combustion engine in which the heating occurs at constant pressure allowing the gas to expand in the ignition of the mixture.
ID:(1487, 0)
The Diesel Cycle
Storyboard 
The Diesel cycle corresponds to an internal combustion engine in which the heating occurs at constant pressure allowing the gas to expand in the ignition of the mixture.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Continuing the analogy to the ERROR:5219,0 for liquids and solids with the heat capacity ($C$) and the mass ($M$):
there is also a specific heat of gases at constant volume ($c_V$) for heating at constant volume with the heat capacity at constant volume ($C_V$):
Following an analogy to the ERROR:5219,0 for liquids and solids with the heat capacity ($C$) and the mass ($M$):
there is also a specific heat at constant pressure ($c_p$) for heating at constant pressure with the heat capacity at constant pressure ($C_p$):
When supplying the heat supplied ($Q_H$), the gas temperature increases from $T_2$ to $T_3$ in an isobaric process (at constant pressure). This implies that we can use the relationship for ERROR:8085 with the heat capacity at constant pressure ($C_p$) and the variación de Temperature ($\Delta T$), expressed by the equation:
This leads us to the values of the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) and the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$) using the formula:
When the absorbed heat ($Q_C$) is removed, the temperature of the gas increases from $T_1$ to $T_4$ in an isobaric process (at constant pressure). This implies that we can use the relationship for ERROR:8085 with the heat capacity at constant volume ($C_V$) and the variación de Temperature ($\Delta T$), which is expressed by the equation:
This leads us to the values of the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$) and the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$) using the formula:
Given that in an adiabatic expansion, the gas satisfies the relationships the volume in state i ($V_i$), the volume in state f ($V_f$), the temperature in initial state ($T_i$), the temperature in final state ($T_f$), and the adiabatic index ($\kappa$) as expressed in:
We can observe that during the state change from the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$) to the compressed volume ($V_2$) and the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$), the following equality holds:
$T_1V_1^{\kappa-1}=T_2V_2^{\kappa-1}$
Using the equation for the compressibility factor ($r_C$):
We obtain:
Given that in an adiabatic expansion, the gas satisfies the relationships the volume in state i ($V_i$), the volume in state f ($V_f$), the temperature in initial state ($T_i$), the temperature in final state ($T_f$), and the adiabatic index ($\kappa$) as expressed in:
We can observe that during the state change from the intermediate volume ($V_3$) and the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) to the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$), the following equality holds:
$T_3V_3^{\kappa-1}=T_4V_1^{\kappa-1}$
By using the equation for the expandability factor ($r_E$):
We obtain:
Since the heating occurs at constant pressure, Charles' law applies:
Therefore, the change of state ($V_2, T_2$) to ($V_3, T_3$) must satisfy:
$\displaystyle\frac{T_2}{V_2} = \displaystyle\frac{T_3}{V_3}$
Using the equations:
we can rewrite it as:
$T_3 = \displaystyle\frac{V_3}{V_2} T_2 = \displaystyle\frac{V_3}{V_2} T_2 = \displaystyle\frac{V_3}{V_1} \displaystyle\frac{V_1}{V_2} T_2 = \displaystyle\frac{r_C}{r_E} T_2$
In other words:
The value of the efficiency ($\eta$) can be calculated using the values the adiabatic index ($\kappa$), the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$), the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$), the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$), and the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$) in the following equation:
Furthermore, the relationships between temperatures with the compressibility factor ($r_C$) and the expandability factor ($r_E$) are defined by the following equations:
Additionally, the value of the adiabatic index ($\kappa$) is used in the equation:
These equations allow us to calculate the performance of a process following the Diesel cycle using the following equation:
In an adiabatic expansion, the gas satisfies the relationship involving the volume in state i ($V_i$), the volume in state f ($V_f$), the temperature in initial state ($T_i$), and the temperature in final state ($T_f$):
In this case, from the initial point 3 to point 4. This means that during the adiabatic expansion, the state of the gas changes from the compressed volume ($V_2$) and the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) to the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$) according to:
Given that in an adiabatic expansion, the gas satisfies the relationship with the volume in state i ($V_i$), the volume in state f ($V_f$), the temperature in initial state ($T_i$), and the temperature in final state ($T_f$):
In this case, from the initial point 1 to point 2. This means that during the adiabatic compression, the state of the gas changes from the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$) to the compressed volume ($V_2$) and the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$) as follows:
The efficiency relationship in terms of temperature is obtained using the definition of efficiency:
and the supplied heat and absorbed heat quantities:
This leads us to the efficiency relationship in terms of temperature:
Examples
The Diesel cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that forms the basis of diesel engines, commonly used in vehicles and industrial machinery. Developed by Rudolf Diesel in the 1890s, this cycle is distinct from the gasoline engine's Otto cycle primarily in its ignition process. In the Diesel cycle, air is drawn into the cylinder and compressed at a much higher ratio than in gasoline engines, which heats it to a temperature that can ignite diesel fuel without the need for a spark plug.
During operation, the cycle starts with the piston drawing in air as it moves downward. The air is then compressed on the upward stroke, raising its temperature. At the peak of the compression phase, fuel is injected into the hot compressed air as a fine mist, causing spontaneous ignition. The combustion forces the piston downward, generating power. Finally, the exhaust phase expels the combustion gases when the piston moves upward again, completing the cycle.
Diesel engines are noted for their efficiency and durability. The high compression ratio not only allows the engine to extract more energy from the fuel but also increases its thermal efficiency, meaning a greater portion of the fuel's energy is converted to mechanical work. Diesel engines typically offer better fuel efficiency and produce fewer CO2 emissions per unit of energy than their gasoline counterparts, but they can emit higher levels of other pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and particulates.
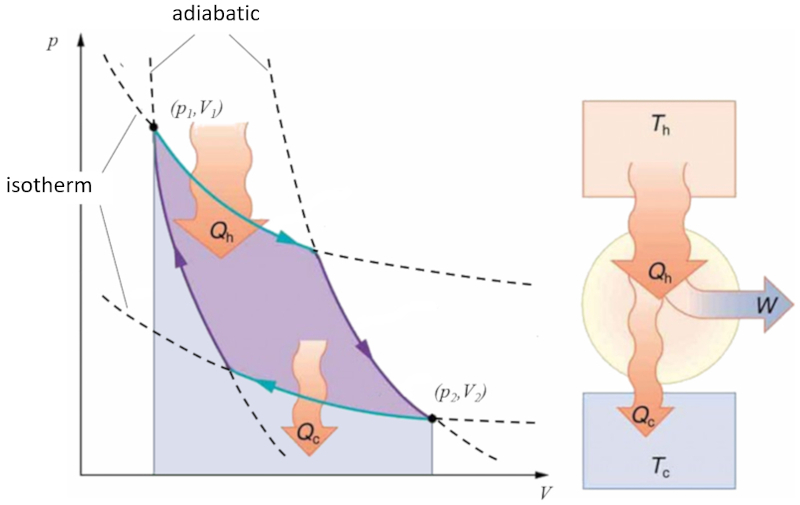
Sadi Carnot introduced [1] the theoretical concept of the first machine design capable of generating mechanical work based on a heat gradient. This concept is realized through a process in the pressure-volume space where heat is added and extracted, as depicted in the image:
The area under curve the heat supplied ($Q_H$), spanning from 1 to 2, represents the energy input required to transition from state ($p_1, V_1$) to state ($p_2, V_2$). Conversely, the area under curve the absorbed heat ($Q_C$), going from 2 to 1, represents the energy extraction needed to return from state ($p_2, V_2$) back to state ($p_1, V_1$). The difference between these areas corresponds to the region enclosed by both curves and represents the effective work ($W$) that the system can perform.
Carnot also demonstrated that, in accordance with the second law of thermodynamics, the heat supplied ($Q_H$) cannot equal zero. This implies that no machine can convert all heat into work.
![]() [1] "R flexions sur la puissance motrice du feu et sur les machines propres d velopper cette puissance" (Reflections on the Motive Power of Fire and on Machines Fitted to Develop That Power), Sadi Carnot, Annales scientifiques de l .N.S. 2e s rie, tome 1, p. 393-457 (1872)
[1] "R flexions sur la puissance motrice du feu et sur les machines propres d velopper cette puissance" (Reflections on the Motive Power of Fire and on Machines Fitted to Develop That Power), Sadi Carnot, Annales scientifiques de l .N.S. 2e s rie, tome 1, p. 393-457 (1872)
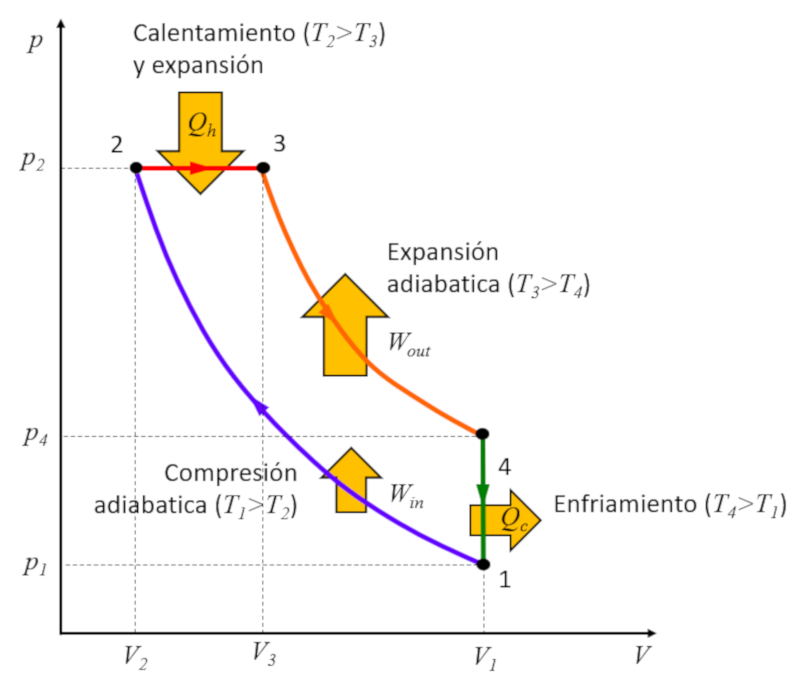
Rudolf Diesel [1] set out to create a cycle distinct from the Carnot cycle with the aim of achieving higher efficiency compared to the Otto cycle. This process unfolds in the following stages:
• Stage 1 to 2: Adiabatic compression $(p_1,V_1,T_1)\rightarrow (p_2,V_2,T_2)$,
• Stage 2 to 3: Heating and expansion at constant pressure $(p_2,V_2,T_2)\rightarrow (p_2,V_3,T_3)$,
• Stage 3 to 4: Adiabatic expansion $(p_2,V_3,T_3)\rightarrow (p_3,V_1,T_4)$,
• Stage 4 to 1: Cooling at constant volume $(p_3,V_1,T_4)\rightarrow (p_1,V_1,T_1)$
These stages are illustrated below:
The key lies in stage 2 to 3, where expansion occurs at constant pressure. The reason becomes evident when examining the graph:
The energy gained is equal to the area enclosed within the cycle, and by performing compression at constant pressure, this area is greater than in the case of compression at constant volume.
![]() [1] "Verfahren zur Entwickelung eines rationellen W rmemotors zum Ersatz der Dampfmaschine und der heute bekannten Verbrennungsmotoren" (Method for the Development of a Rational Heat Engine to Replace the Steam Engine and Contemporary Combustion Engines), Rudolf Diesel, Kaiserlichen Patentamts, No. 67207 (1892)
[1] "Verfahren zur Entwickelung eines rationellen W rmemotors zum Ersatz der Dampfmaschine und der heute bekannten Verbrennungsmotoren" (Method for the Development of a Rational Heat Engine to Replace the Steam Engine and Contemporary Combustion Engines), Rudolf Diesel, Kaiserlichen Patentamts, No. 67207 (1892)
Both the Otto cycle and the Diesel cycle rely on variables the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$), the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$), the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$), and the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$). However, in the case of the Diesel cycle, it also depends on the adiabatic index ($\kappa$), whose value is 1.4.
In the Otto cycle, efficiency is calculated based on temperature using the equation:
While in the Diesel cycle, efficiency is calculated based on temperature using the equation:
The inclusion of the factor $1/\kappa \sim 0.71$ in the Diesel cycle makes it more efficient compared to the Otto cycle for the same temperature configuration. This is a direct result of enlarging the area enclosed in the curve that represents the cycle in the pressure-volume representation.
Given that in an adiabatic expansion, the gas satisfies the relationships the volume in state i ($V_i$), the volume in state f ($V_f$), the temperature in initial state ($T_i$), the temperature in final state ($T_f$), and the adiabatic index ($\kappa$) as expressed in:
We can observe that during the state change from the intermediate volume ($V_3$) and the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) to the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$), the following equality holds:
$T_3V_3^{\kappa-1}=T_4V_1^{\kappa-1}$
By using the equation for the expandability factor ($r_E$):
We obtain:
Given that in an adiabatic expansion, the gas satisfies the relationships the volume in state i ($V_i$), the volume in state f ($V_f$), the temperature in initial state ($T_i$), the temperature in final state ($T_f$), and the adiabatic index ($\kappa$) as expressed in:
We can observe that during the state change from the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$) to the compressed volume ($V_2$) and the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$), the following equality holds:
$T_1V_1^{\kappa-1}=T_2V_2^{\kappa-1}$
Using the equation for the compressibility factor ($r_C$):
We obtain:
Since the heating occurs at constant pressure, Charles' law applies:
Therefore, the change of state ($V_2, T_2$) to ($V_3, T_3$) must satisfy:
$\displaystyle\frac{T_2}{V_2} = \displaystyle\frac{T_3}{V_3}$
Using the equations:
we can rewrite it as:
$T_3 = \displaystyle\frac{V_3}{V_2} T_2 = \displaystyle\frac{V_3}{V_2} T_2 = \displaystyle\frac{V_3}{V_1} \displaystyle\frac{V_1}{V_2} T_2 = \displaystyle\frac{r_C}{r_E} T_2$
In other words:
The efficiency relationship in terms of temperature is obtained using the definition of efficiency:
and the supplied heat and absorbed heat quantities:
This leads us to the efficiency relationship in terms of temperature:
The value of the efficiency ($\eta$) can be calculated using the values the adiabatic index ($\kappa$), the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$), the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$), the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$), and the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$) in the following equation:
Furthermore, the relationships between temperatures with the compressibility factor ($r_C$) and the expandability factor ($r_E$) are defined by the following equations:
Additionally, the value of the adiabatic index ($\kappa$) is used in the equation:
These equations allow us to calculate the performance of a process following the Diesel cycle using the following equation:
In this case, from the initial point 1 to point 2. This means that during the adiabatic compression, the state of the gas changes from the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$) to the compressed volume ($V_2$) and the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$) as follows:
The heat supplied ($Q_H$) can be calculated with the heat capacity at constant pressure ($C_p$), the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) and the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$) using the formula:
In this case, from the initial point 3 to point 4. This means that during the adiabatic expansion, the state of the gas changes from the compressed volume ($V_2$) and the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) to the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$) according to:
The absorbed heat ($Q_C$) can be calculated from the heat capacity at constant volume ($C_V$), the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$) and the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$) using the formula:
In the analysis of the Diesel cycle, it is helpful to introduce the so-called the compressibility factor ($r_C$), which represents the relationship between the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the compressed volume ($V_2$) during the compression of the mixture, as shown in the following expression:
In the analysis of the Diesel cycle, it is advantageous to introduce the term the expandability factor ($r_E$), which represents the relationship between the expanded volume ($V_1$) and the intermediate volume ($V_3$) during the compression of the mixture, as illustrated in the following expression:
The temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) can be calculated with the temperature in state 4 ($T_4$), the expandability factor ($r_E$) and the adiabatic index ($\kappa$) using:
The temperature in state 2 ($T_2$) can be calculated from the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$), the compressibility factor ($r_C$) and the adiabatic index ($\kappa$) using:
The temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) can be calculated from the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$), the compressibility factor ($r_C$) and the expandability factor ($r_E$) using:
The efficiency ($\eta$) can be calculated from the adiabatic index ($\kappa$), the temperature in state 1 ($T_1$), the temperature in state 2 ($T_2$), the temperature in state 3 ($T_3$) and 8492 using:
The calculation of the efficiency ($\eta$) is performed using the adiabatic index ($\kappa$), the compressibility factor ($r_C$) and the expandability factor ($r_E$), as follows:
The specific heat at constant pressure ($c_p$) is equal to the heat capacity at constant pressure ($C_p$) divided by the mass ($M$):
The specific heat of gases at constant volume ($c_V$) is equal to the heat capacity at constant volume ($C_V$) divided by the mass ($M$):
ID:(1487, 0)