Cross Product or Vector Product
Storyboard 
The so-called cross product or vector product allows to determine an orthogonal vector to the vectors that create it. Its magnitude corresponds to twice the area that would have a rectangle with sides equal to the magnitudes of each of the vectors.
ID:(1259, 0)
Graphical representation of the cross product
Definition 
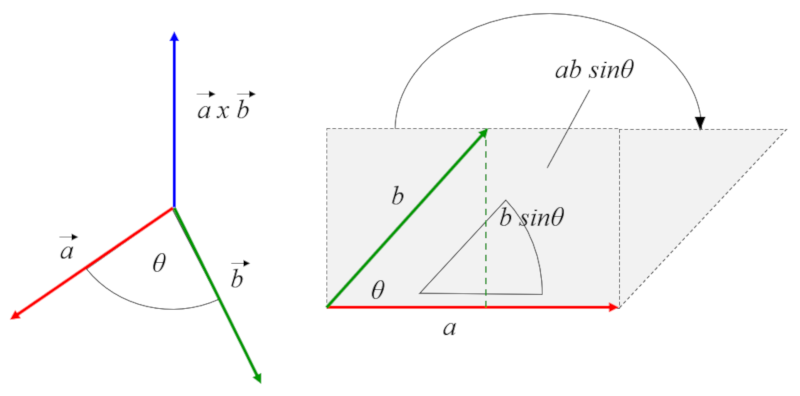
The cross product generates a vector that is orthogonal to those that generate it and whose magnitude is the multiplication of the magnitudes of each vector and the sine of the angle between them.
The length of the resulting vector corresponds to the area of the parallelepiped formed by the two vectors that generate it:
ID:(4582, 0)
Cross Product or Vector Product
Description 
The so-called cross product or vector product allows to determine an orthogonal vector to the vectors that create it. Its magnitude corresponds to twice the area that would have a rectangle with sides equal to the magnitudes of each of the vectors.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
The cross product generates a vector that is orthogonal to those that generate it and whose magnitude is the multiplication of the magnitudes of each vector and the sine of the angle between them.
The length of the resulting vector corresponds to the area of the parallelepiped formed by the two vectors that generate it:

(ID 4582)
El producto cruz se puede definir como una determinante de una matriz cuyas lineas son los versores del sistema
| $ \vec{a}\times\vec{b} =( a_y b_z - a_z b_y , a_z b_x - a_x b_z , a_x b_y - a_y b_x )$ |
(ID 3676)
Si se expresa el producto cruz en funci n del versor
| $ \mid\vec{a}\times\vec{b}\mid = \mid\vec{a}\mid \mid\vec{b}\mid \sin \theta $ |
donde
(ID 3677)
ID:(1259, 0)
