Heat exchange
Storyboard 
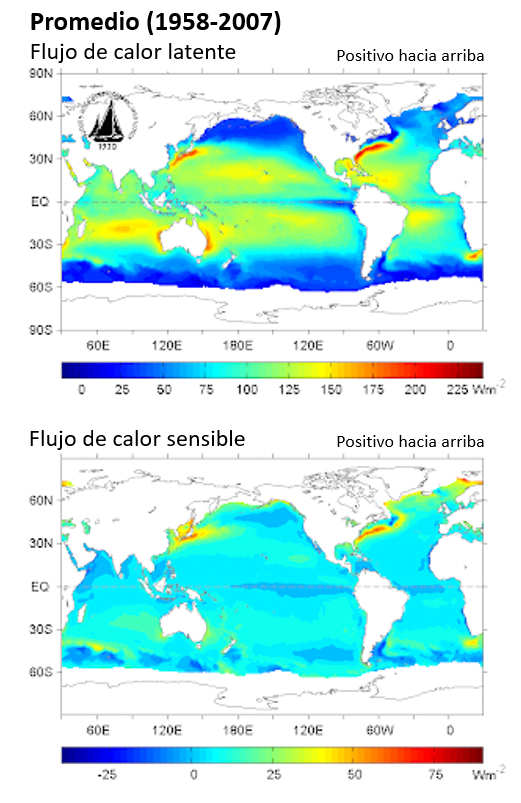
The exchange of heat between the atmosphere and the ocean refers to the process by which the atmosphere transfers or absorbs heat from the ocean, thereby equalizing the temperatures between the two.
Ocean-Atmosphere Interactions of Gases and Particles, Peter S. Liss, Martin T. Johnson (eds.). Springer, 2014
Chapter: Transfer Across the Air-Sea Interface
ID:(1580, 0)
Heat exchange
Storyboard 
The exchange of heat between the atmosphere and the ocean refers to the process by which the atmosphere transfers or absorbs heat from the ocean, thereby equalizing the temperatures between the two. Ocean-Atmosphere Interactions of Gases and Particles, Peter S. Liss, Martin T. Johnson (eds.). Springer, 2014 Chapter: Transfer Across the Air-Sea Interface
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
In the Monin-Obukhov Similarity Theory (MOST), the surface heat energy, represented by
$\rho_a c_p (T_z - T_0)$
is transferred to the water with the transfer coefficient $C_H$ and the air velocity $U_z$, resulting in the heat flux.
Examples
In the case of heat flux, the heat content is estimated using density, specific heat, and temperature, along with the wind velocity and the transmission coefficient. In this way, the heat flux can be expressed as follows:
La energ a disipada se puede estimar de la viscosidad, densidad y grosor de la capa.
Por ello con
El grosor de la superficie y de la capa viscosas son proposicionales siendo la constante una funci n de la constante difusi n, viscosidad y densidad.
Por ello con
ID:(1580, 0)